In today's digital age, organizations are constantly threatened by cyber threats, and one of the most powerful enemies they face is the Advanced Persistent Threat (APT). APTs represent a class of cyberattacks characterized by persistence, sophistication, and targeting. Unlike malicious attacks, APTs do not try to move quickly; They are patient and willing to invest significant time and resources to participate in the campaign. In this blog post, we will dive into the world of APTs, uncover their characteristics, understand their existence, and give you the information and ideas you need to identify and protect them.
Understanding Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are a class of cyberattacks distinguished by their persistence, advanced tactics, and targeted nature. Here's what sets them apart:
- Persistence: As the name suggests, APTs are persistent and patient in their pursuit of their objectives. These attackers are willing to bide their time and stay undetected for extended periods, sometimes for years.
- Advanced Tactics: APT actors employ highly advanced and sophisticated techniques to breach defenses. They often use zero-day exploits, custom-made malware, and targeted spear-phishing campaigns.
- Targeted Approach: Unlike random attacks, APTs have specific victims in mind. They choose their targets carefully, often focusing on organizations, industries, or even individuals. Their attacks are precisely tailored to their chosen victims.
- Concealment: APT actors operate covertly. They employ encryption, anti-forensic methods, and evasion tactics to remain hidden from security measures.
The APT Lifecycle
Understanding the APT lifecycle is crucial in detecting and defending against these threats. It typically consists of the following phases:
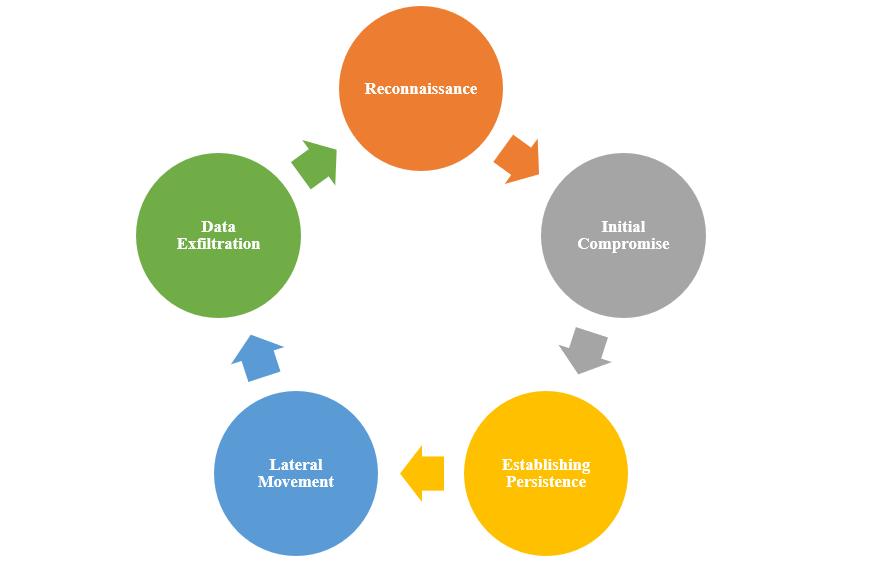
- Reconnaissance: Attackers gather information about their target, identifying vulnerabilities and potential entry points.
- Initial Compromise: APTs gain entry through various means, including spear-phishing, watering hole attacks, or exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Establishing Persistence: Once in, they establish backdoors or footholds to ensure continuous access.
- Lateral Movement: APTs move laterally through the network, looking for valuable data and spreading their influence.
- Data Exfiltration: Finally, stolen data is stealthily sent to servers controlled by the attackers.
Detection Strategies for APTs
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitor network and system behavior for unusual or suspicious activities. A deviation from the norm can be an indicator of APT activity.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Stay updated on known APT campaigns and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) through threat intelligence sources.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Use EDR solutions to keep an eye on endpoints, looking for signs of APT activity like unusual processes or file changes.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Analyze user and entity behavior for deviations from established patterns, which may indicate APT presence.
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into segments to limit lateral movement opportunities for APTs.
Effective Defense Strategies
- Zero Trust Architecture: Assume zero trust, requiring verification from anyone or anything attempting to access resources.
- Regular Patch Management: Keep software and systems up-to-date to prevent attackers from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about APTs and the importance of cybersecurity hygiene, especially regarding social engineering attacks.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical assets and segments from the rest of the network to reduce the attack surface.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to detect, contain, eradicate, and recover from APT incidents.
- Deception Technology: Employ deception tactics, such as honeypots and honey tokens, to lure and identify APT intruders.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security, making unauthorized access more challenging for APT actors.
Conclusion
Advanced Persistent Threats represent a persistent and significant danger to organizations across the globe. Understanding their characteristics, using effective detection techniques, and strong defenses are key to fending off these formidable enemies. Cybersecurity is an ongoing battle, and it is crucial to be vigilant, flexible, and prepared to protect an organization's data and digital assets from the APT threat. Defending the door against these attackers is more than an attack; This is important in today's connected world. Stay calm and stay safe.



