


A deadlock in operating systems is a situation where two or more processes are unable to proceed because each one is waiting for a resource that the other processes hold. It's like a standstill where each process is blocking the others, creating a cycle of dependency that can't be resolved on its own.
Example:
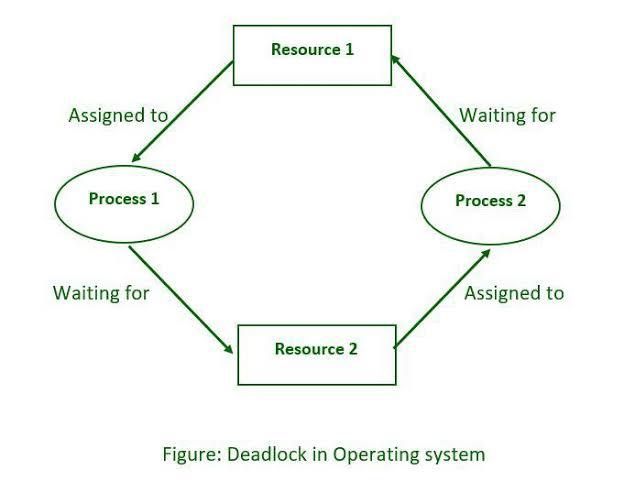
Imagine two processes, Process A and Process B, and two resources, Resource 1 and Resource 2. Here’s how a deadlock might occur:
1. Process A locks Resource 1 (say, a file).
2. Process B locks Resource 2 (for example, a printer).
3. Process A now needs Resource 2 to continue its work, so it waits for Process B to release it.
4. Process B, on the other hand, needs Resource 1 to complete its task, so it waits for Process A to release it.
The Deadlock:
- Process A is waiting for Resource 2, which is held by Process B.
- Process B is waiting for Resource 1, which is held by Process A.
Since neither process can proceed without the other releasing a resource, they are stuck in a deadlock.
The Four Conditions for Deadlock:
For a deadlock to occur, four specific conditions must be met:
1. Mutual Exclusion:
At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode. In other words, only one process can use the resource at a time.
2. Hold and Wait:
A process is holding at least one resource and waiting to acquire additional resources that are currently being held by other processes.
3. No Preemption:
Resources cannot be forcibly taken from a process; they must be released voluntarily by the process holding them.
4. Circular Wait:
A set of processes are waiting for each other in a circular chain. Each process is waiting for a resource that the next process in the chain holds.
Handling Deadlocks:
Operating systems use various strategies to handle deadlocks, including:
- Deadlock Prevention:
Ensuring that at least one of the four necessary conditions for deadlock cannot occur.
- Deadlock Avoidance:
Dynamically analyzing resource allocation to ensure that a circular wait condition does not develop.
- Deadlock Detection:
Allowing deadlocks to occur but having mechanisms to detect and resolve them, often by terminating one or more of the processes involved.
- Deadlock Recovery:
Once a deadlock is detected, the system can take actions like forcibly reclaiming resources or terminating processes to break the cycle.
In summary, a deadlock is a problematic situation in operating systems where processes are stuck indefinitely, waiting for resources held by each other, making it impossible for them to continue execution.