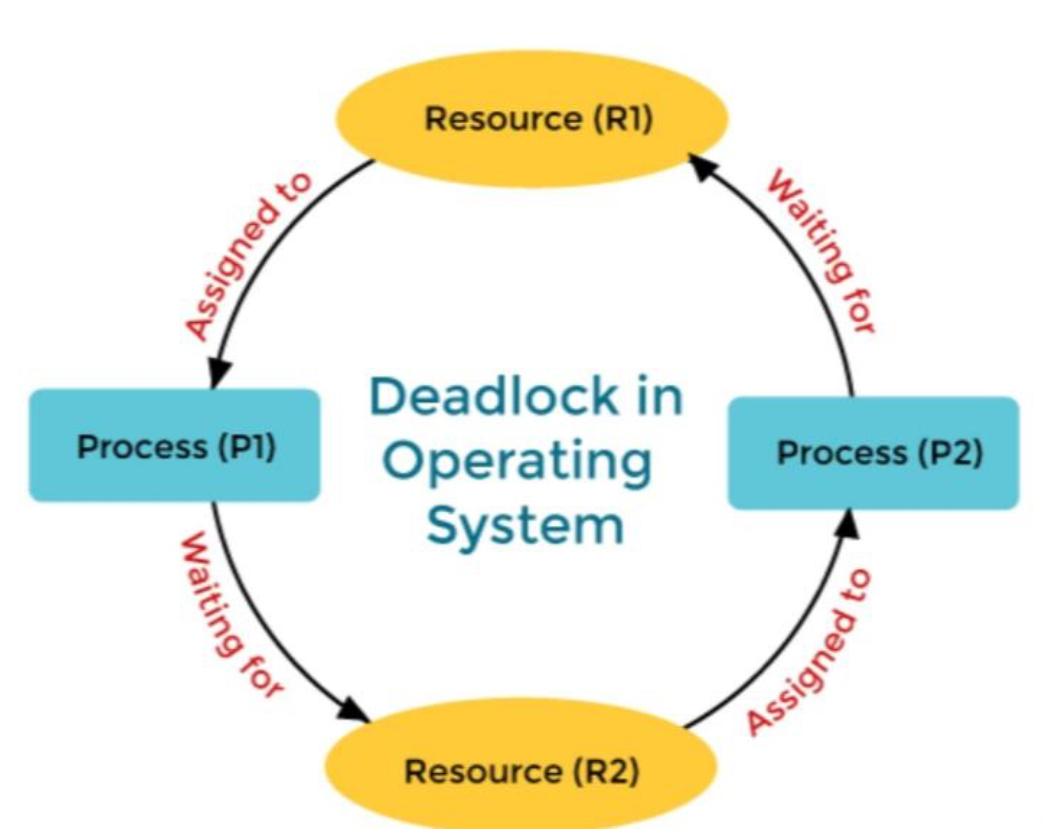
A deadlock in an operating system is a situation where a set of processes become stuck, unable to proceed because each process is waiting for a resource that another process in the same set is holding. Since none of the processes can proceed until another releases its resources, they are in a state of perpetual waiting, leading to a deadlock.
Key Conditions for Deadlock:
A deadlock can occur if the following four conditions hold simultaneously:
- Mutual Exclusion: At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode, meaning only one process can use the resource at a time.
- Hold and Wait: A process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources that are currently being held by other processes.
- No Preemption: A resource cannot be forcibly removed from a process holding it; it can only be released voluntarily by the process holding it.
- Circular Wait: A set of processes exist where each process is waiting for a resource that the next process in the chain holds, forming a circular chain of dependencies.
Example Scenario:
Imagine two processes, P1 and P2, and two resources, R1 and R2. Suppose:
- P1 holds R1 and requests R2.
- P2 holds R2 and requests R1.
In this situation, P1 and P2 are waiting on each other to release the resources, leading to a deadlock.
Deadlock Handling Strategies:
Operating systems handle deadlocks using one of the following approaches:
- Deadlock Prevention: Ensuring that at least one of the four conditions for deadlock cannot occur.
- Deadlock Avoidance: Using algorithms (like the Banker’s algorithm) to ensure that the system never enters an unsafe state where a deadlock might occur.
- Deadlock Detection and Recovery: Allowing deadlocks to occur, but the system periodically checks for deadlocks and takes action to recover, such as terminating one or more processes involved in the deadlock.
- Ignoring the Problem: Some systems, especially simple ones or those where deadlocks are rare, choose to ignore the problem, hoping that deadlocks will not occur frequently.