


Deadlock in an operating system is a complex situation where a set of processes are blocked because each process is holding resources and waiting for resources held by other processes. This condition causes a system to come to a halt, as no process can proceed. Here's a detailed explanation of the concept:
### Key Concepts:
1. **Processes**: These are programs in execution that require resources to complete their tasks. Resources could be hardware (like printers or memory) or software resources (like file handles).
2. **Resources**: These are entities required by processes to perform operations. Resources can be:
- **Preemptive**: Can be taken from a process (e.g., CPU time).
- **Non-preemptive**: Cannot be taken from a process without its consent (e.g., printers, files).
### Deadlock Conditions (Coffman Conditions):
To understand deadlock, consider the following four necessary conditions that must all hold true simultaneously:
1. **Mutual Exclusion**: Only one process can use a resource at any given time. If a process holds a resource, no other process can use it until it is released.
2. **Hold and Wait**: Processes holding resources can request additional resources. This means that a process may be holding some resources while waiting to acquire more.
3. **No Preemption**: Resources cannot be forcibly taken from processes holding them. A resource can only be released voluntarily by the process holding it.
4. **Circular Wait**: There is a circular chain of processes, where each process is waiting for a resource held by the next process in the chain.
### Examples:
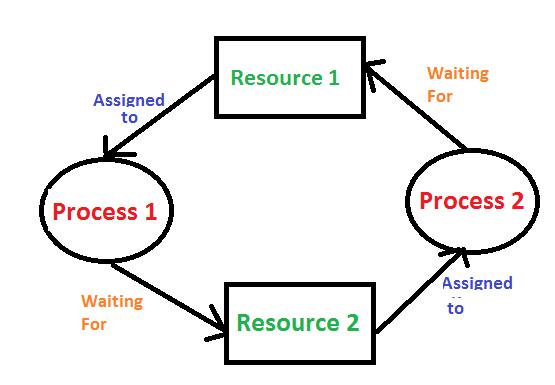
- **Resource Allocation**: Consider two processes, P1 and P2. P1 holds resource R1 and requests resource R2, while P2 holds R2 and requests R1. This circular wait condition causes a deadlock.
- **Dining Philosophers Problem**: In this classic example, five philosophers sit at a table with a fork between each pair. Each philosopher needs both forks to eat. If each philosopher picks up one fork and waits for the other, a deadlock occurs if all five are waiting for forks simultaneously.
### Deadlock Handling Strategies:
1. **Deadlock Prevention**: This approach ensures that at least one of the Coffman conditions is not satisfied. For example:
- **Avoiding Hold and Wait**: Require processes to request all the resources they need at once, reducing the chance of holding some while waiting for others.
- **Ensuring No Circular Wait**: Impose a linear ordering of resources and require that processes request resources in that order.
2. **Deadlock Avoidance**: This strategy dynamically checks the resource allocation state to ensure that a circular wait condition never occurs. One well-known algorithm for this is the Banker's Algorithm, which requires knowledge of maximum resource needs in advance.
3. **Deadlock Detection**: This involves allowing deadlock to occur and then detecting it using algorithms that check for cycles in the resource allocation graph. Once detected, the system takes action to resolve the deadlock, typically by terminating or preempting processes.
4. **Deadlock Recovery**: After detecting a deadlock, recovery strategies include:
- **Process Termination**: Abort one or more processes to break the cycle.
- **Resource Preemption**: Take resources away from some processes and allocate them to others to break the circular wait.
In practice, deadlock handling often involves a combination of these strategies to balance system performance and reliability.