


Deadlock is a situation in computing and concurrent systems where a set of processes are unable to proceed because each process is waiting for resources held by another process, creating a cycle of dependencies that cannot be resolved. In essence, it’s a standstill where processes are stuck indefinitely.
To understand deadlock more clearly, let’s break it down into its core components:
1. **Conditions for Deadlock**:
Deadlock occurs when four necessary conditions are met simultaneously:
- **Mutual Exclusion**: At least one resource must be held in a non-shareable mode, meaning only one process can use the resource at a time.
- **Hold and Wait**: A process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources currently held by other processes.
- **No Preemption**: Resources cannot be forcibly taken from a process; they must be released voluntarily.
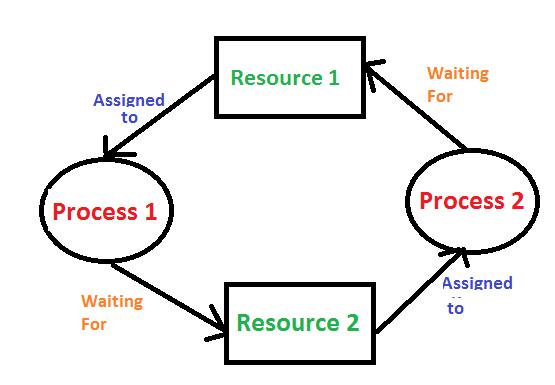
- **Circular Wait**: A set of processes are waiting for each other in a circular chain. For example, Process A waits for a resource held by Process B, Process B waits for a resource held by Process C, and Process C waits for a resource held by Process A.
2. **Detection and Prevention**:
- **Deadlock Prevention**: Methods involve designing the system to ensure that at least one of the necessary conditions for deadlock cannot hold. For example, by using resource allocation policies that avoid circular wait.
- **Deadlock Avoidance**: Systems can use algorithms like Banker's Algorithm to ensure that resource allocation decisions are made in such a way that the system remains in a safe state, avoiding deadlock.
- **Deadlock Detection**: The system periodically checks for deadlock states using algorithms that analyze the resource allocation graph or other criteria to detect cycles.
- **Recovery**: Once detected, methods to recover from deadlock involve terminating one or more processes or preempting resources from processes to break the circular wait.
3. **Examples**:
- **Dining Philosophers Problem**: A classic example in which philosophers seated at a table must pick up two forks to eat, but each philosopher holds one fork and waits for the other, leading to a deadlock if all are waiting for the fork held by their neighbor.
- **Resource Allocation Systems**: In database systems or operating systems, where processes request multiple resources, the possibility of deadlock arises if resources are not managed carefully.
Overall, deadlock is a critical concept in operating systems, databases, and distributed systems, requiring careful management to ensure system reliability and performance.