



In the interconnected digital landscape, security and accessibility of online systems are critical due to the widespread sharing and accessing of services and information. Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks stand out as a significant threat, aiming to disrupt systems by overwhelming resources or exploiting vulnerabilities, rendering them inaccessible to authorized users. The evolution of technology has empowered malicious actors with innovative tools, expanding the scope of DoS attacks beyond network floods to include application-layer attacks targeting software weaknesses. This article explores various DoS attack techniques and offers prevention strategies to safeguard online assets, providing security experts and decision-makers with insights to bolster digital infrastructure.
WHAT IS DENIAL-OF-SERVICE OR DISTRIBUTED DENIAL-OF-SERVICE?
Denial-of-Service (DoS) refers to a cyber attack strategy where malicious actors intentionally overwhelm a target system's resources or exploit vulnerabilities, causing it to become inaccessible to legitimate users, disrupting its normal functioning.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks involve multiple sources coordinating to amplify the attack's impact, making mitigation more complex.
DOS/DDOS ATTACK TYPES:
There are three primary types of DoS attacks, distinguished mainly by the type of traffic they lob at victims’ systems:
Volumetric Attacks: Overwhelm with massive data, deplate bandwidth and resources.
Application Layer Attacks: Target app vulnerabilities, exhaust computational resources.
Protocol-Based Attacks: Exploit communication flaws, flood connection requests.
DOS/DDOS ATTACK TECHNIQUES:
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks encompass a range of techniques aimed at disrupting the availability of online services and systems. These techniques exploit vulnerabilities in various layers of network infrastructure to overwhelm resources and render services inaccessible. Some common DoS attack techniques include:
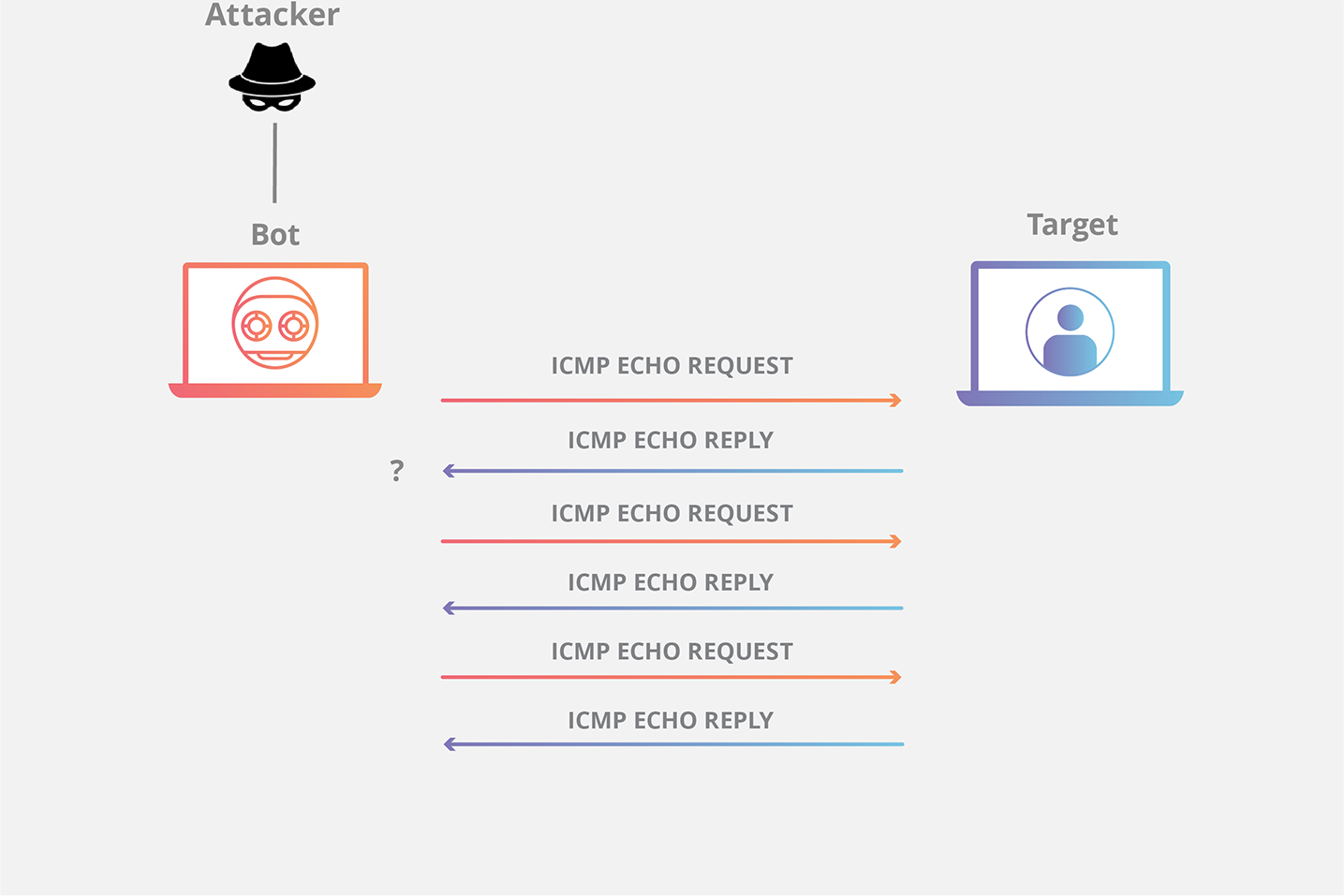
Attackers inundate a target's network with a high volume of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request (Ping) packets. The target's resources become consumed with processing and responding to these requests, leading to network congestion and service disruption.
SYN/ACK Floods:
This attack targets the TCP three-way handshake process. Attackers send a massive number of SYN (synchronize) requests without completing the handshake by sending the necessary ACK (acknowledge) responses. The target's resources are tied up waiting for the responses, leading to resource exhaustion.
UDP Floods:
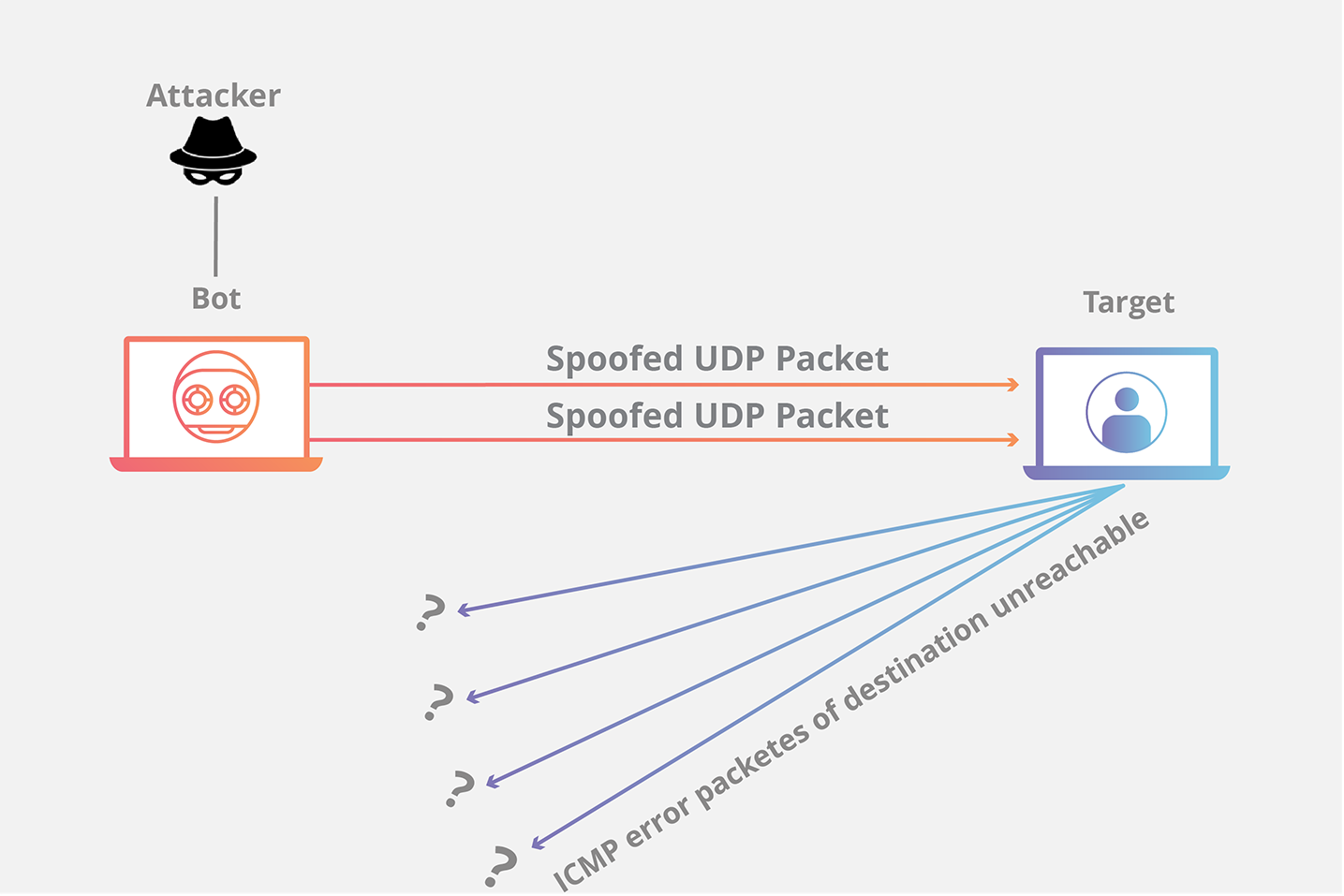
Attackers flood a target with User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets, often from random source IP addresses. UDP, being connectionless, requires fewer resources to initiate connections than TCP, allowing attackers to overwhelm the target's resources more easily.
DNS Amplification Attacks:
Attackers send forged DNS queries to open DNS servers with a spoofed victim's IP address. The servers then respond with larger DNS responses, amplifying the attack traffic and overloading the target's network.
HTTP/S Floods:
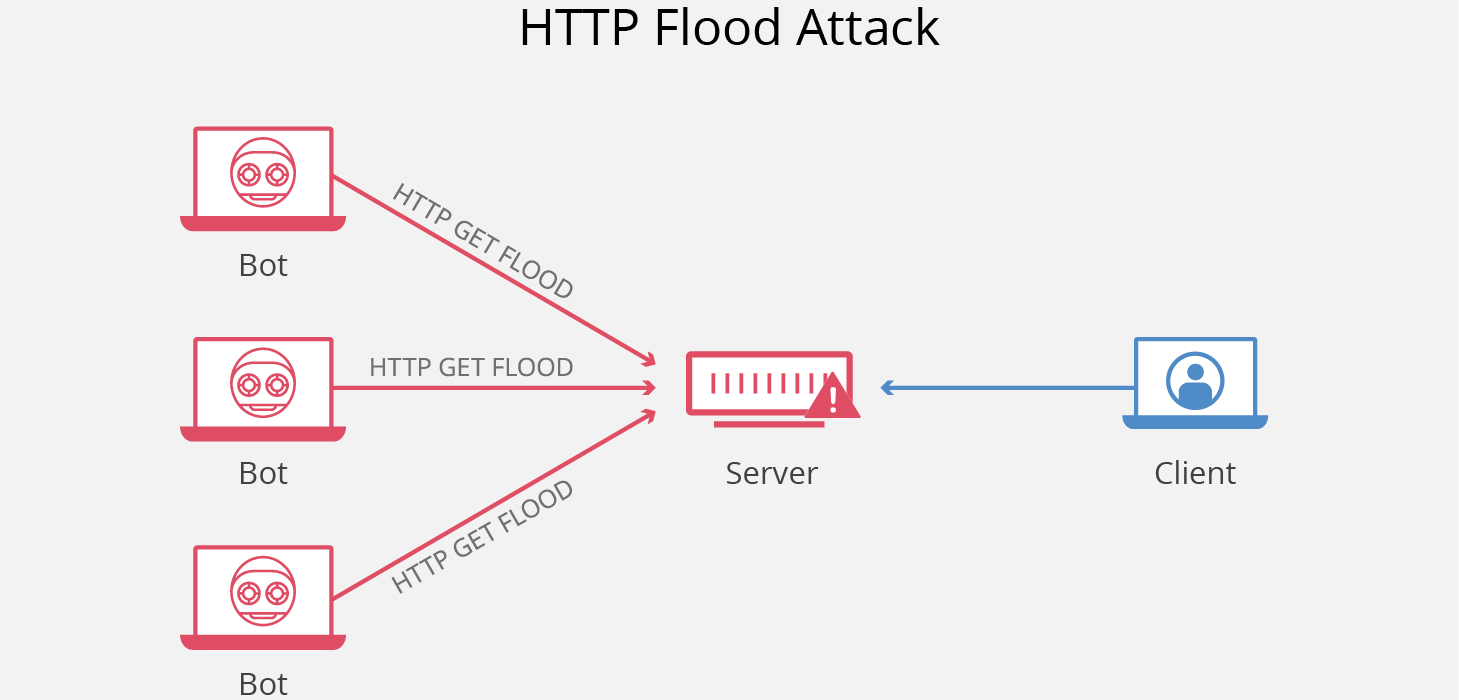
Attackers flood web servers with a high volume of legitimate-looking HTTP or HTTPS requests. The servers become overwhelmed as they try to process each request, leading to slowdowns or service unavailability.
Slow Loris Attacks:
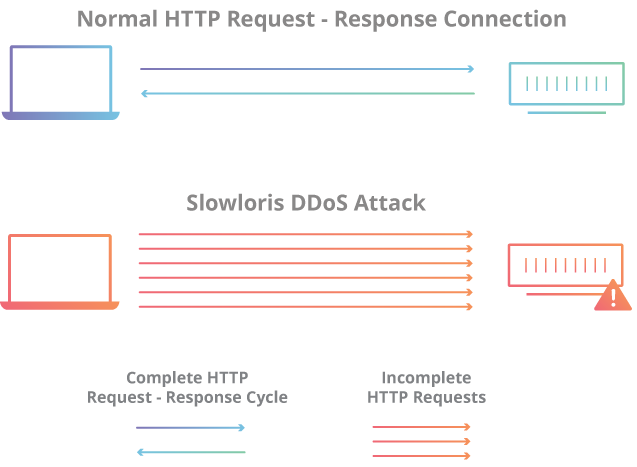
Attackers exploit the fact that web servers keep connections open while waiting for a complete request. By sending partial requests and keeping connections open with minimal traffic, the attacker ties up server resources and prevents new connections.
Smurf Attacks:
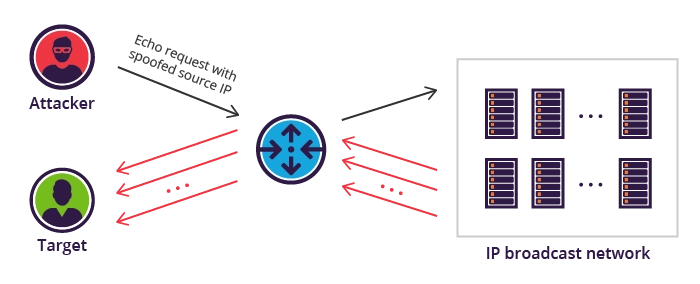
Attackers send ICMP echo requests (pings) with the victim's IP address as the source to broadcast networks. The responses from all devices on the network flood back to the victim, causing network congestion.
MITIGATION STRATEGIES:
Certainly, here are few specific mitigation strategies for combating Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack techniques:
Rate Limiting and Traffic Shaping: Control network traffic by setting limits and prioritizing certain data, ensuring optimal resource allocation and preventing congestion.
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Safeguard web applications by filtering and monitoring incoming HTTP traffic, shielding them from various cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
Cloud-Based Solutions and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Enhance performance and security by distributing content through globally distributed servers, reducing latency and enabling scalability.
Behavioral Analysis and Anomaly Detection: Identify deviations from normal patterns in user or network behavior, helping to detect potential security breaches or abnormalities.
Protecting online systems from the constant threat of Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks is of the highest priority in the ever-expanding digital world. Our defense methods must change as these attacks become more sophisticated and larger in scope. We may create a strong barrier against disruption by understanding the complex nature of attack types and methodologies and by putting into place effective mitigation strategies. We secure the reliability and use of our digital infrastructure for future generations by combining technological innovation and proactive security.