


Linux Memory Management
Linux's memory management system is intricate, sharing several characteristics with other UNIX-like systems but also featuring unique attributes. It handles process virtual memory, kernel memory allocation, page allocation, and page replacement with considerable sophistication.
Linux Virtual Memory
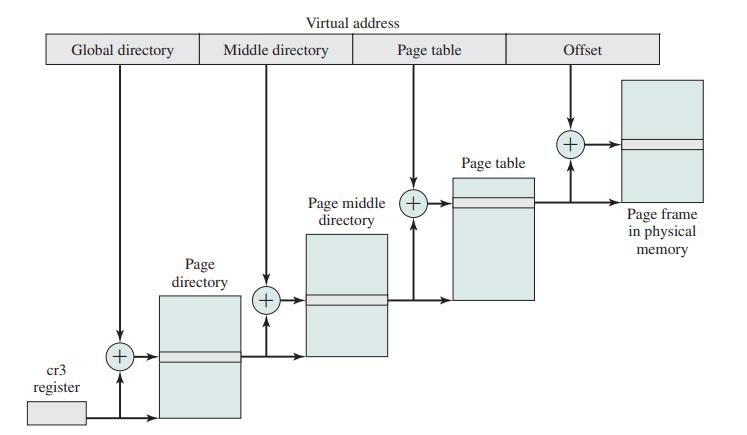
Virtual Memory Addressing
Linux uses a three-level page table structure to manage virtual memory, which includes:
Page Allocation
Page allocation is crucial for the efficient use of memory. Linux uses the Buddy System for allocating memory at the kernel level. This system divides memory into blocks that are powers of two, which can then be split or merged as needed to satisfy memory allocation requests. For user-space processes, Linux allocates memory on a page-by-page basis, using the slab allocator for small objects and frequently requested memory blocks, reducing fragmentation and improving performance.
Address Translation in Linux Virtual Machine Scheme.
Page Replacement Algorithms
When physical memory becomes full, Linux must decide which pages to remove from memory to make room for new pages. This decision is made using page replacement algorithms. The most commonly used algorithms in Linux include:
Least Recently Used (LRU):
- LRU is a commonly used page replacement algorithm in Linux. It tracks the order in which pages are accessed and replaces the least recently used pages when new pages need to be loaded. The assumption is that pages that haven't been used recently are less likely to be used in the immediate future.
Clock Algorithm:
- A variant of LRU, the clock algorithm is less resource-intensive. Pages are arranged in a circular list, and a "hand" moves around the list. If a page’s "use" bit is set, it is cleared, and the hand moves to the next page. If the bit is not set, that page is replaced. This balances efficiency with the need to approximate LRU behavior.
Kernel Memory Allocation
Kernel memory allocation differs from user-space memory allocation, requiring efficiency and speed. The Buddy System and Slab Allocator are employed to manage kernel memory. The Buddy System is used for larger memory allocations, minimizing fragmentation, while the Slab Allocator handles small, frequently used memory objects.
Conclusion
Linux's memory management system is designed to handle complex computing environments efficiently. The system uses a multi-level page table structure, sophisticated kernel memory allocation strategies, and effective page replacement algorithms to maintain optimal performance. By balancing these mechanisms, Linux ensures that both user processes and kernel operations run smoothly, even under heavy memory demands.