


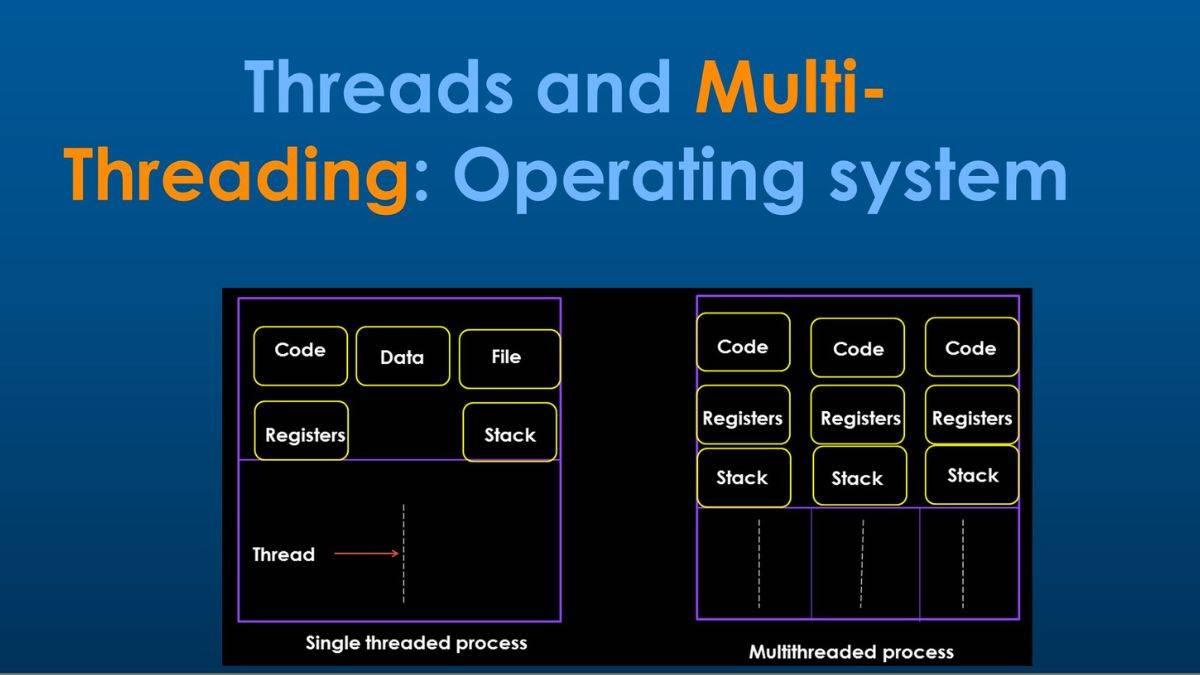
Thread refers to the smallest unit of execution within a process. It is a sequence of instructions that can be scheduled and executed independently by the CPU. Threads exist within the context of a process and share the same memory space and resources allocated to that process.
Multithreading is a fundamental concept in computer science and software development that allows programs to execute multiple threads concurrently within a single process. Each thread represents a separate flow of control, enabling applications to perform tasks in parallel, thereby utilizing available resources more efficiently and potentially improving performance. We can make the following distinction:
• Thread: A dispatchable unit of work. It includes a processor context (which
includes the program counter and stack pointer) and its own data area for a
stack (to enable subroutine branching). A thread executes sequentially and is
interruptable so that the processor can turn to another thread.
• Process: A collection of one or more threads and associated system resources
(such as memory containing both code and data, open files, and devices). This
corresponds closely to the concept of a program in execution. By breaking
a single application into multiple threads, the programmer has great control
over the modularity of the application and the timing of application-related
events.
One of the primary advantages of multithreading is its ability to improve the performance of applications. For example, in a web server, multithreading enables the handling of multiple client requests simultaneously, reducing latency and improving the user experience. Similarly, in graphical user interfaces (GUIs), multithreading allows the interface to remain responsive while performing background operations like data processing or file downloads.
However, multithreading is not without its challenges. One of the primary issues is synchronization, which ensures that multiple threads do not interfere with each other when accessing shared resources. Improper synchronization can lead to problems like race conditions, where the outcome of a program depends on the timing of thread execution, potentially causing unpredictable behavior. To address this, developers use synchronization mechanisms like locks, semaphores, and condition variables to coordinate thread access to shared resources.
In conclusion, multithreading is a crucial technique for improving the performance and efficiency of modern computing applications. By allowing concurrent execution of multiple threads, it leverages the full potential of multi-core processors and enhances the responsiveness of applications. Despite its challenges, such as synchronization and deadlock, effective use of multithreading can lead to significant gains in computational speed and resource utilization, making it an indispensable tool in the realm of software development.