


Computer security concept :
∆ Computer security is also known as Cybersecurity, involves protecting computer system and network from theft, damage, and unauthorised access .
∆ The goal is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems.
Here are the key components:
Confidentiality: Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information. Techniques like encryption and access controls are used to ensure that only authorized users can view certain data.
Integrity: Ensures that data and systems are not interface with in an unauthorized manner. Methods such as checksums and digital signatures help verify that information remains unchanged.
Availability: Ensures that systems and data are accessible to authorized users when needed. This involves protecting against disruptions such as hardware failures, cyber attacks, or natural disasters
Additional aspects include:
Authentication: Verifying the identity of users and devices.
Authorization: Granting permissions to users based on their identity and roles.
Auditing: Keeping logs of system activities to detect and respond to security incidents.
Non-repudiation: Ensuring that actions or transactions cannot be denied by the parties involved, often achieved through digital signatures.
Overall, computer security involves a combination of technologies, policies, and practices designed to protect digital assets from various threats.
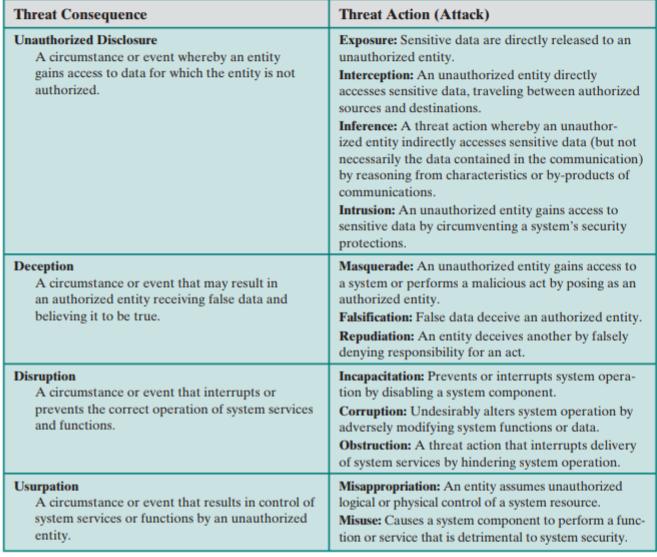
*** THREATS, ATTACKS, AND ASSETS
Let's cover some examples of this topic :-
Unauthorized Disclosure
Consequence: Sensitive data is accessed by someone who shouldn't have it.(Apna important data koi aur access karleta hai jiske paas nhi jana chahiye uske paas bhi chala jaata hai )
Threat Actions:
1. Exposure:
- Example: A healthcare provider accidentally publishes patient records online without proper security, making them accessible to anyone.
2. Interception:
- Example: A hacker uses a network sniffer to capture data packets traveling over a public Wi-Fi network, gaining access to sensitive information such as login credentials.
3. Inference:
- Example: By analyzing patterns of communication between executives, an attacker deduces the timing of a merger announcement, even though the content of the communications was encrypted.
4. Intrusion:
- Example: An attacker exploits a vulnerability in a web application to bypass security controls and access a database containing customer personal information.
Usurpation
Consequence: Control of system services or functions is taken over by an unauthorized entity.(Ismei kisi unauthorised person ke paas control chala jata hai system service or functions ka )
Threat Actions:
1. Misappropriation:
- Example: An attacker gains control of a company's server and uses it to mine cryptocurrency, consuming resources and potentially exposing sensitive data.
2. Misuse:
- Example: A disgruntled employee installs software on a company server to send spam emails, using the organization's resources for malicious purposes and damaging its reputation.