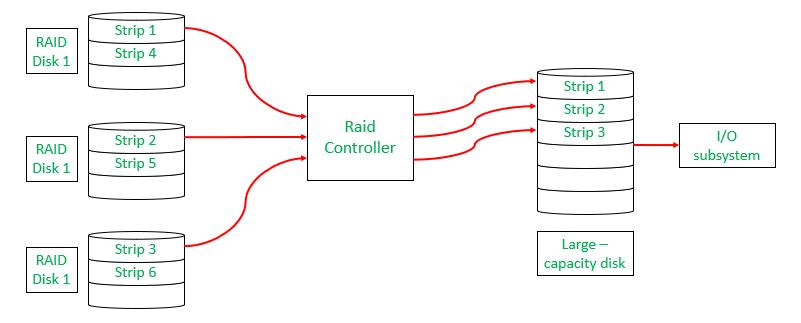
RAID( spare Arrays of Independent Disks) makes use of a combination of multiple disks for storing the data rather of using a single fragment for increased performance, data redundancy, or to cover data in the case of a drive failure. A RAID controller works between your computer’s operating system and the factual hard drives, organizing them into groups to make them easier to manage. This helps speed up how presto your computer can read and write data, and it also adds a subcaste of protection in case one of your hard drives breaks down.
Levels of RAID
- RAID 0 ( Striping ) : RAID 0 spreads data across multiple disks( at least two) in a way that enhances data read/ write speeds. still, there's no redundancy in this configuration, meaning that if one fragment fails, all data in the array is lost.

- RAID 1 ( Mirroring ) : RAID 1 involves using a minimum of two disks to produce an exact dupe( glass) of data from one fragment to another. It provides data redundancy.

- RAID 2 : This configuration uses striping across disks, with some disks storing error checking and correcting( ECC) information. RAID 2 also uses a devoted Hamming law equality, a direct form of ECC.

- RAID 3 : This technique uses striping and dedicates one drive to storing equality information. The embedded ECC information is used to descry crimes. Because an I/ O operation addresses all the drives at the same time, RAID 3 can not lap I/ O. For this reason,RAID 3 is best for single-user systems with long record applications

- RAID 4 : This position uses large stripes, which means a stoner can read records from any single drive. Lapped I/ O can also be used for read operations. Because all write operations are needed to modernize the parity drive, no I/O lapping is possible.

- RAID 5 (Striping with Parity) : RAID 5 distributes data and parity information (used for error correction and redundancy) across at least three disks. It offers improved read performance and fault tolerance. If one disk fails, the data can be reconstructed using the parity information stored on other disks.

- RAID 6 (Striping with Double Parity) : RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5 but provides additional fault tolerance by using double parity information. This means that RAID 6 can withstand the failure of two disks simultaneously without losing data.