


Segmentation and Paging in Operating Systems
Segmentation and paging are two fundamental techniques employed by operating systems to manage memory efficiently. While they share the common goal of optimizing memory utilization, they differ significantly in their approaches.
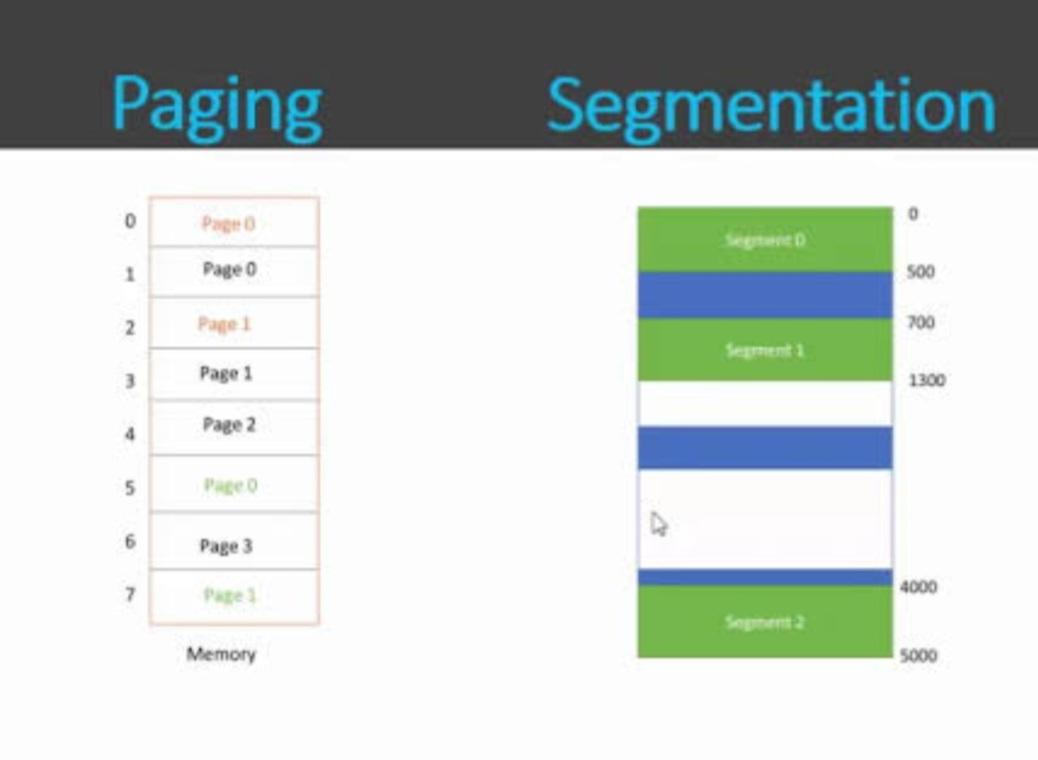
1.Segmentation
• Divides memory into variable-sized segments.
• Segments correspond to logical units: code, data, stack, heap, etc.
• Provides flexibility: Allows efficient allocation of memory based on program structure.
• Protection: Enables access control at the segment level.
• Sharing: Facilitates sharing of code and data segments among processes.
Example: A program might have separate segments for instructions, global variables, and local variables.
2.Paging
• Divides physical memory into fixed-sized blocks called pages.
• Divides processes into fixed-sized pages as well.
• Simplifies memory management: Treats memory as a uniform structure.
• Overcomes external fragmentation: Efficiently utilizes available memory.
• Enables virtual memory: Allows processes to use more memory than physically available.
Example: A process’s address space is divided into pages, which are mapped to physical frames in memory.
Maitry Gala-53003230041
Div A