


Memory partitioning in an operating system (OS) is a technique used to manage memory allocation by dividing the system's physical memory into distinct regions, or partitions. Each partition can be allocated to processes or the operating system itself. Memory partitioning is crucial for optimizing memory utilization and ensuring that multiple processes can run efficiently without interfering with each other. There are several memory partitioning schemes, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Here's a detailed explanation of the key concepts:
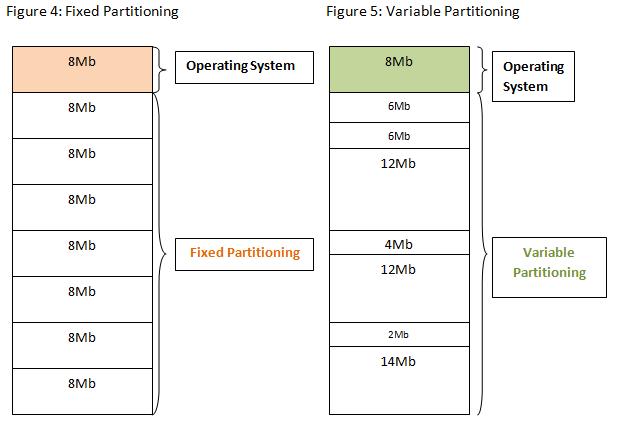
1. Fixed Partitioning Definition: In fixed partitioning, the memory is divided into a fixed number of partitions at system startup. The size and number of partitions are predefined.
• Advantages:
Simple to implement.
Low overhead for partition management.
• Disadvantages:
Inefficient use of memory because a process may be allocated a partition larger than its actual needs (internal fragmentation).
The number of partitions limits the number of processes that can be loaded into memory simultaneously.
Types:
1. Equal-size partitions: All partitions are of the same size.
2. Unequal-size partitions: Partitions vary in size, allowing for more flexible allocation but still suffer from internal fragmentation.
2. Dynamic partitioning Definition: Unlike fixed partitioning, dynamic partitioning creates partitions dynamically at runtime based on the needs of processes. When a process is loaded into memory, a partition is created that exactly matches its size.
• Advantages:
Better memory utilization as partitions match the process size, reducing internal fragmentation.
• Disadvantages:
Leads to external fragmentation, where free memory is scattered in small blocks, making it difficult to find contiguous space for large processes.
Requires complex management algorithms to keep track of free and allocated spaces.
3. Simple paging: Main memory is divided into a number of equal-size frames. Each process is divided into a number of equal-size pages of the same length as frames. A process is loaded by loading all of its pages into available, not necessarily contiguous, frames.
• Advantages:
No external fragmentation.
• Disadvantages:
A small amount of internal fragmentation.
4. Simple segmentation: Each process is divided into a number of segments. A process is loaded by loading all of its segments into dynamic partitions that need not be contiguous.
• Advantages:
No internal fragmentation; improved memory utilization and reduced overhead compared to dynamic partitioning.
• Disadvantages:
External fragmentation.
5. Buddy System: The buddy system is a memory allocation algorithm that divides memory into partitions to minimize fragmentation. It works by dividing memory into blocks that are powers of two and pairs them as "buddies."
• Advantages:
Efficient for dynamic memory allocation and deallocation.
Minimizes external fragmentation by combining free blocks (buddies).
• Disadvantages:
Can still suffer from internal fragmentation, as processes may be allocated slightly larger memory blocks than needed.
Complexity in merging and splitting blocks.
6. Virtual Memory Paging: As with simple paging, except that it is not necessary to load all of the pages of a process. Nonresident pages that are needed are brought later automatically.
• Advantages:
No external fragmentation;
higher degree of multiprogramming; large virtual address space.
• Disadvantages:
Overhead of complex memory management.
7. Virtual Memory Segmentation: As with simple segmentation, except that it is not necessary to load all of the segments of a process. Nonresident segments that are needed are brought in later automatically.
• Advantages:
No internal fragmentation, higher degree of multiprogramming; large virtual address space; protection and sharing support.
• Disadvantages:
Overhead of complex memory management.