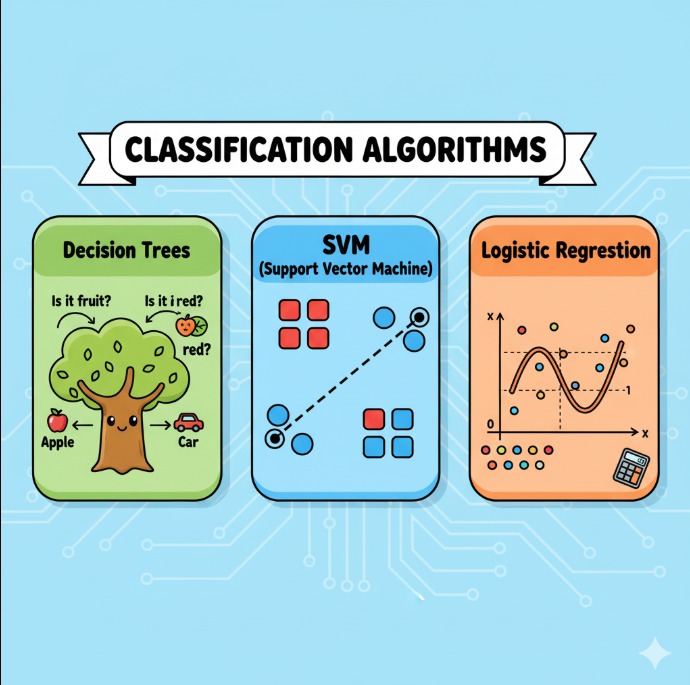
What are Classification Algorithms?
Classification is a method in Data Science where we predict which category or group a data point belongs to. For example, predicting whether an email is spam or not, or whether a patient has a disease
1. Decision Trees
How it works:
- Works like a question-answer game.
- It asks questions like “Is age > 30?” and splits data into branches.
- The last leaf gives the final class (answer).
Use cases:
- Predict if a customer will leave
- Medical diagnosis
- Loan/credit risk check
Pros (good points):
- Very easy to understand
- Works with numbers and text
- Less data cleaning needed
Cons (bad points):
- Can overfit (memorize training data too much)
- Small changes in data can make a very different tree
2.Support Vector Machines (SVM)
How it works:
- Imagine you have red and blue dots on paper.
- SVM draws a line (boundary) to separate them with maximum distance between groups.
- This line is called a hyperplane.
Use cases:
- Image recognition
- Text categorization (like spam detection)
- Bioinformatics (like classifying proteins)
Pros (good points):
- Works well when there are many features
- Memory efficient (uses less space)
Cons (bad points):
- Not good for very large datasets
- Not good with noisy or overlapping data
3.Logistic Regression
How it works:
- Gives a probability between 0 and 1 using an S-shaped curve (sigmoid)
- If probability is > 0.5 → class A, else class B
Use cases:
- Spam detection
- Disease prediction
- Will a customer buy a product or not
Pros (good points):
- Simple, fast, and easy
- Easy to explain
Cons (bad points):
- Works best when data is linear
- Sensitive to outliers (unusual data points)