


Concurrency:
Concurrency refers to the ability of the Operating Systems to execute multiple of processes or threads simultaneously for making efficient usage of CPU time/resources.
Processes are nothing but an instance of a program that is running with its own memory space.
OSes uses Context Switching mechanism to implement concurrency. It is the process of saving the current state of a currently executing process or thread and restoring other process or thread. This allows OS to switch between tasks giving an illusion of simultaneous execution.
Concurrency in OS leads to problems like Deadlock and Starvation.
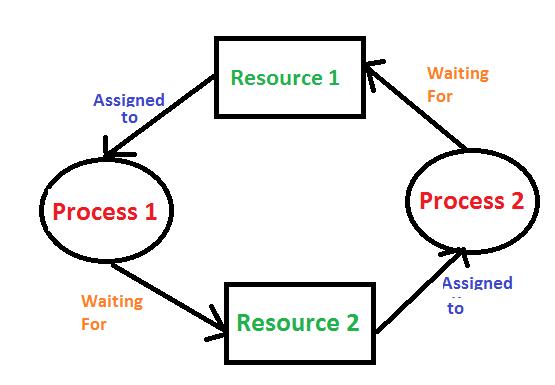
Deadlock:
A deadlock is a situation when two are more processes are unable to proceed because each process is waiting for other to release a resource. This leads to a state where none of the processes can continue and they’re stuck indefinitely.
Deadlocks occur when several conditions are met simultaneously:
Mutual Exclusion: Resources are not shared and can be allocated to only one process at a time.
Hold and Wait: A process holding particular resources can request additional resources without releasing currently held.
No Preemption: Resources cannot be taken forcibly from resources and they must be freed simultaneously.
Circular Chain: A circular chain of process where processes wait for other to release resources held by them.
Deadlock Prevention:
Deadlock prevention ensures that at least one of the four conditions will not come true and will not lead to a deadlock from occurring.
Prevent Mutual Exclusion: Design systems where minimum number of resources are non-shareable, or convert non-shareable resources to shareable ones if possible reducing the probability of having deadlock.
Prevent Hold and Wait: Processes should request all the necessary resources before execution. If all resources not available it waits for them.
Prevent No Preemption: Allow pre-emption of resources where necessary to break deadlock conditions. If P2 needs a resource that P1 holds, P1 is forced to release its resource and wait until both resources are available. The system preempts P1, breaking the deadlock condition.
Prevent Circular Wait: Give each resource a unique priority. A process can only request resources in increasing order of their priority. This ensures there is always a linear dependency preventing circular wait.
Deadlock Avoidance:
Deadlock Avoidance dynamically decisions are made whether the granting the resource will potentially lead a deadlock.
A process is not granted a resource if it might lead to a deadlock.
Deadlock avoidance allows processes to request resources that prevents the system from entering a deadlock.