Vulnerability:
vulnerability in networking are the security weeknesses or loop holes that gives threats the opportunity to compromises assests, like software, hardware, or organizational processes can result in a security breach.
Types of vulnerability:
Hardware:
Outdated Computer: The problem with old outdated computers is that a lot of it's equipment doesn't have built-in security features, self-healing basic input/output system (BIOS), preboot authentication, self-encrypting drivers and the like.
Old routers: Routers that manufactured in 2011 and earlier- can have serious vulnerabilities.
Drivers that don't self-encrypt: Self encrypt drivers requires a password in addition to the OS login password, and the technology automatically encrypts and decrypts data on the drive.
Software:
Unpatched or out-of-date Operating systems: The OS that does not have automatic updates or technical assistance, latest security updates and the OS that has fewer security features than more modern OSes are prone to attack easier.
Malicious code: A common vulnerability is the potential for remote code execution when a user opens or previews a maliciously prepared files or visits a website containing content that exploits the vulnerability.
Missing or weak Authorization Credentials: A common tactic that attackers use is to gain access to systems and networks through brute force like guessing employee credentials. That is why it is crucial that employees be educated on the best practices of cybersecurity so that their login credentials are not easily exploited.
Social engineering attacks: Social engineering attack that fool users into giving up personal information such as a username or password.
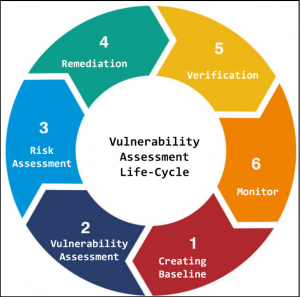
Vulnerability assessments Life Cycle: