


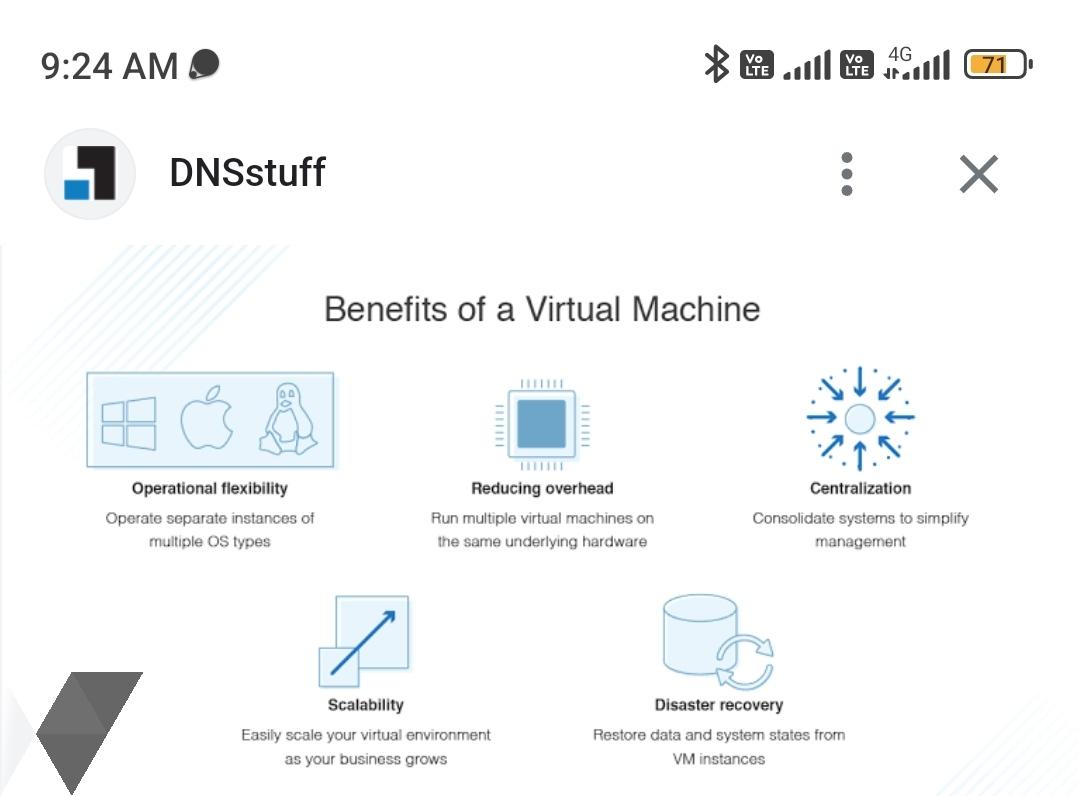
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination of the two. Virtual machines differ and are organized by their function,System virtual machines provide a substitute for a real machine.A hypervisor uses native execution to share and manage hardware, allowing for multiple environments that are isolated from one another yet exist on the same physical machine. Modern hypervisors use hardware-assisted virtualization, with virtualization-specific hardware features on the host CPUs providing assistance to hypervisors.
Process virtual machines are designed to execute computer programs in a platform-independent environmentA virtual machine (VM) is a virtual environment that functions as a virtual computer system with its own CPU, memory, network interface, and storage, created on a physical hardware system. Software called a hypervisor separates the machine’s resources from the hardware and provisions them appropriately so they can be used by the VM.
The physical machines, equipped with a hypervisor such as Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), is called the host machine, host computer, host operating system, or simply host. .