


Memory Management Techniques: -
Process Isolation:
Each running program gets its own section of memory. The OS must prevent independent processes from interfering with each other’s memory, both data and instructions.This prevents processes from interfering with each other.
Virtual Memory:
Think of virtual memory as an imaginary extension of your computer’s actual RAM. When RAM is full, the OS moves some data to the hard drive. This allows bigger programs to run as if they have more memory than they really do.
Swapping:
If there’s too much demand on memory, the OS can move entire processes from RAM to the hard drive to free up space. It’s like temporarily moving out of your apartment to let someone else use it for a bit.
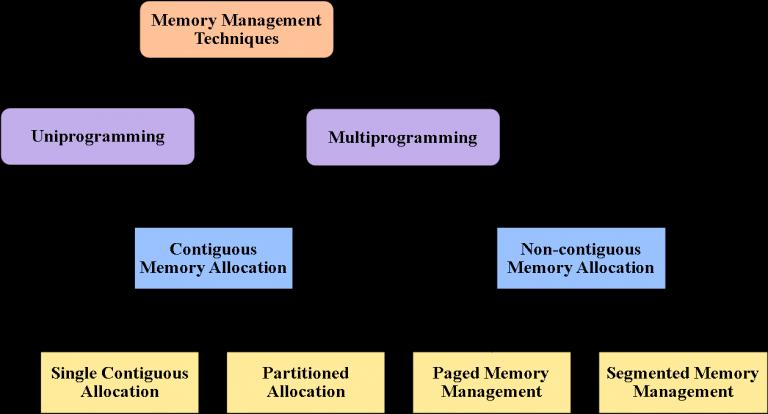
There are two types of Memory Allocation Techniques:-
A) Contiguous Allocation:
Memory is allocated in a single, continuous block. Simple and fast, but can waste space or memory as processes end and start.
B)Non-Contiguous Allocation:
Memory is allocated in separate blocks scattered around, using various techniques like segmentation. More efficient use of space but more complex to manage.
Cache Management:
Uses small, fast memory caches to store frequently accessed data, speeding up the overall performance of the system. Imagine it as having a few frequently used Application pinned on your PC Tab bar instead of searching for them.
Protection and access control:
Sharing of memory, at any level of the memory hierarchy, creates the potential for one program to address the memory space of another. This is desirable when sharing is needed by particular applications. At other times, it threatens the integrity of programs and even of the OS itself. The OS must allow portions of memory to be accessible in various ways by various users.
Summary: In essence, memory management in an operating system is about organizing and optimizing the use of memory to ensure that programs run efficiently and reliably. It involves allocating memory to processes, moving data between RAM and storage as needed, and protecting memory spaces to maintain system stability and security.