


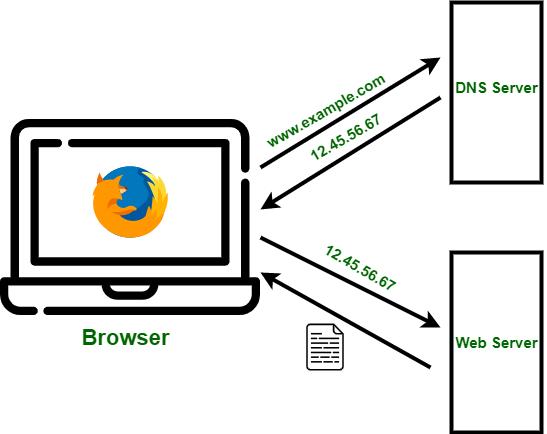
The Domain Name System (DNS) turns domain names into IP addresses, which browsers use to load internet pages. Every device connected to the internet has its own IP address, which is used by other devices to locate the device. DNS servers make it possible for people to input normal words into their browsers, such as Fortinet.com, without having to keep track of the IP address for every website.
A DNS server is a computer with a database containing the public IP addresses associated with the names of the websites an IP address brings a user to. DNS acts like a phonebook for the internet. Whenever people type domain names, like Yahoo.com, into the address bar of web browsers, the DNS finds the right IP address. The site’s IP address is what directs the device to go to the correct place to access the site’s data.Once the DNS server finds the correct IP address, browsers take the address and use it to send data to content delivery network (CDN) edge servers or origin servers. Once this is done, the information on the website can be accessed by the user. The DNS server starts the process by finding the corresponding IP address for a website’s uniform resource locator (URL).