


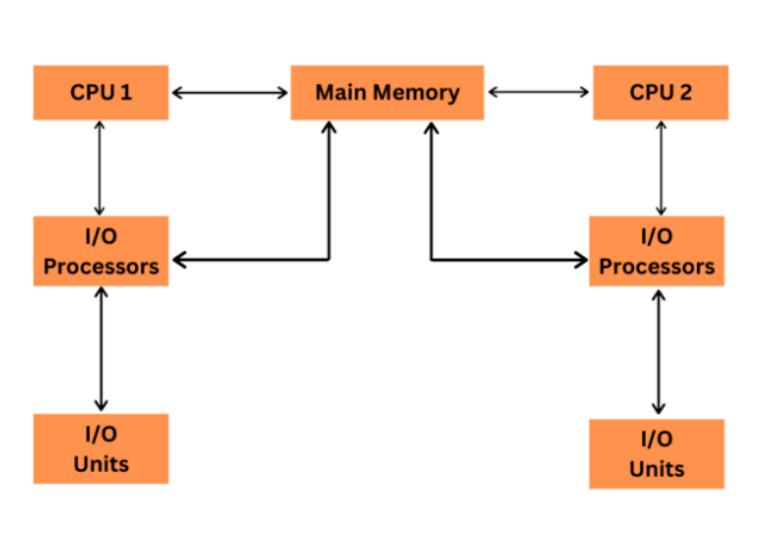
Multiple processor scheduling or multiprocessor scheduling focuses on designing the system's scheduling function, which consists of more than one processor. Multiple CPUs share the load (load sharing) in multiprocessor scheduling so that various processes run simultaneously. In general, multiprocessor scheduling is complex as compared to single processor scheduling. In the multiprocessor scheduling, there are many processors, and they are identical, and we can run any process at any time.
The multiple CPUs in the system are in close communication, which shares a common bus, memory, and other peripheral devices. So we can say that the system is tightly coupled. These systems are used when we want to process a bulk amount of data, and these systems are mainly used in satellite, weather forecasting, etc.
Approaches to Multiple Processor Scheduling
There are two approaches to multiple processor scheduling in the operating system: Symmetric Multiprocessing and Asymmetric Multiprocessing.
Types of Multiprocessor Scheduling Algorithms
Round-Robin Scheduling − The round-robin scheduling algorithm allocates a time quantum to each CPU and configures processes to run in a round-robin fashion on each processor. Since it ensures that each process gets an equivalent amount of CPU time, this strategy might be useful in systems wherein all programs have the same priority.
Priority Scheduling − Processes are given levels of priority in this method, and those with greater priorities are scheduled to run first. This technique might be helpful in systems where some jobs, like real-time tasks, call for a higher priority.
Scheduling with the shortest job first (SJF) − This algorithm schedules tasks according to how long they should take to complete. It is planned for the shortest work to run first, then the next smallest job, and so on. This technique can be helpful in systems with lots of quick processes since it can shorten the typical response time.
Fair-share scheduling − In this technique, the number of processors and the priority of each process determine how much time is allotted to each. As it ensures that each process receives a fair share of processing time, this technique might be helpful in systems with a mix of long and short processes.
Use Cases of Multiple Processors Scheduling in Operating System