



The IoT brings internet connectivity, data processing and analytics to the world of physical objects.The phrase "Internet of Things" describes the overall network of interconnected gadgets as well as the technology that enables communication between gadgets and the cloud as well as among gadgets.
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is made up of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors, and communication gear, to gather, send, and act on the data they get from their surroundings. By connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device, which either sends data to the cloud for analysis or analyses it locally, IoT devices exchange the sensor data they collect. These gadgets converse with other similar devices on occasion, acting on the data they exchange. Although individuals can engage with the devices to set them up, give them instructions, or retrieve the data, the gadgets accomplish the majority of the job without their help.
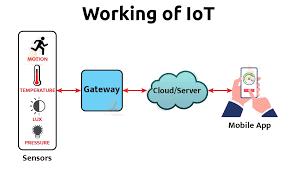
Any device that can gather and transmit information about the physical world can participate in the IoT ecosystem. Smart home appliances, RFID tags, and industrial sensors are a few examples. Other examples include fitness wearables and home security systems. There are also more generic devices, like the RaspberryPi or Arduino, that let you build your own IoT endpoints.