


Definition:-
Fault tolerance in operating systems refers to the ability of a system to continue functioning properly in the event of the failure of some of its components. In simpler words Fault tolerance is a process that enables an operating system to respond to a failure in hardware or software.
Working:-
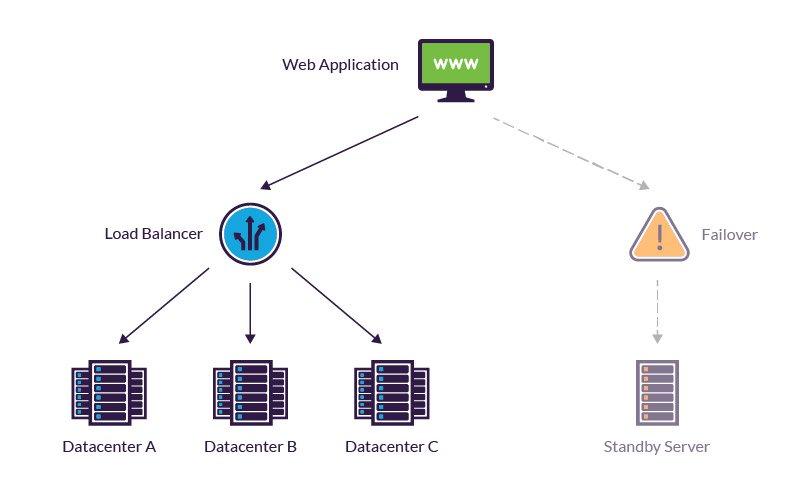
Fault tolerance can be built into a system to remove risk of having single point of failure. A system with fault tolerance should not have any component that if it were to stop working effectively would lead to entire system failing.
It relies on aspects like load balancing and failover which removes the risks of single point of failure. These will be a part of the operating systems interface .This follows two core models:-
Normal Functioning:-
This is when a fault tolerant system encounters a fault but continues to function as usual. Means system sees no change in performance metrics like throughput or response time.
Graceful degradation:-
The other type of fault tolerant system will go through degradation of performance when certain faults occur. It means the impact the fault causes on the system is proportionate to the fault severity. Small fault will have a small impact on systems performance rather than causing the failure of the entire system.
Core components to improving fault tolerance:-
Redundancy:-
This involves duplicating critical components such as processor, memory, or storage devices so that if one fails another can take over seamlessly.
Diverse Architecture:-
Diverse Architecture may be employed to ensure that failures caused by common modes in one architecture are unlikely to affect others.
Fault isolation:-
Modern operating system often uses techniques to isolate faults from spreading and affecting the entire operating system. This involves using virtualization or sandboxing techniques.
Error detection and recovery:-
An operating system incorporates mechanism to detect errors. This can involve error checking codes timeout mechanism etc. Upon the detection system can attempt to recover by re-executing a failed operation.
Components of Fault Tolerance system:-
Hardware System:-
Hardware systems can be backed up by systems that are identical or equivalent to them. A typical example is a server made fault-tolerant by deploying an identical server that runs in parallel to it and mirrors all its operations such as redundant array of inexpensive disk(RAID).
Software Systems:-
Software systems can be made fault-tolerant by backing it up with some other software. A common example is backing up a database that contains data to ensure it can continuously replicate onto another machine.
Power sources:-
Power source can also be made fault-tolerant by using alternative sources to support them. One approach is to run devices on an uninterruptable power supply(UPS). Another is to use backup power generator ,heating ventilation air conditioning(HVAC) continue to operate if primary power source fails.
Factors to consider in fault tolerance system
Cost
Quality Degradation
Testing and fault-detection difficulties