


Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Introduction:
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems that allows some hardware devices (either internal or external) to communicate directly with another computer system’s RAM memory and transfer data from it without processing it using the CPU.This is beneficial for improving the efficiency and speed of data transfers in a system.
In the earlier times, when data needs to be transferred between the memory and a device (like a hard drive or sound card), the CPU has to be involved in each step of the process. This means the CPU reads the data from the device and writes it to memory, or vice versa. This can be slow and inefficient because the CPU gets tied up with these data transfers.
DMA Controller :
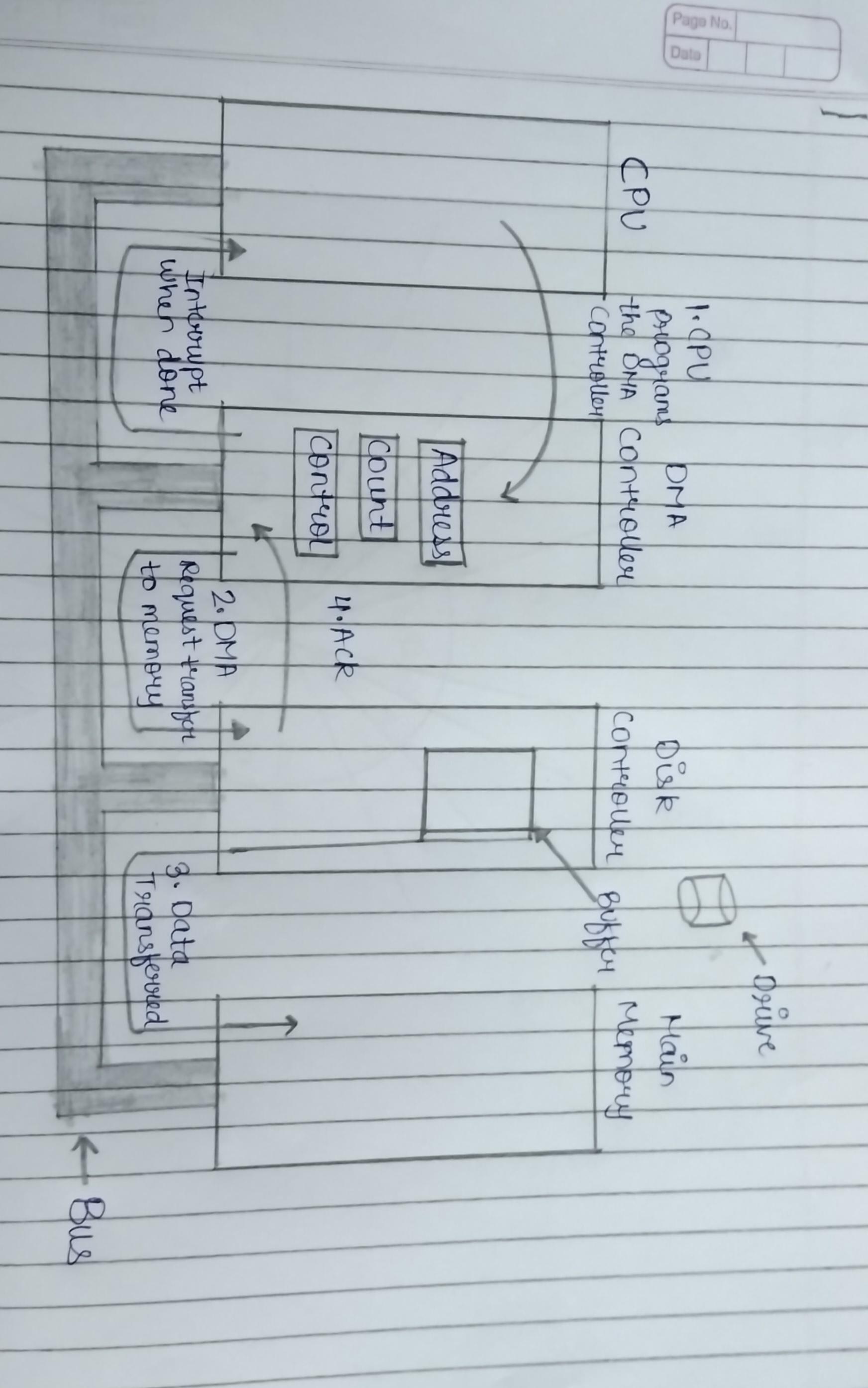
Thus, the DMA controller, a special hardware component, takes over the task of transferring data. The CPU sets up the DMA controller by specifying the source, destination, and the amount of data to transfer. Once configured, the DMA controller handles the data transfer directly, freeing the CPU to perform other tasks.
Working :
In this, The CPU initializes the DMA controller by setting up the source address (where the data is coming from), the destination address (where the data is going), and the length of data to be transferred.
Once initialized, the DMA controller starts the transfer. It takes the data directly from the source and writes it to the destination without CPU intervention.
When the transfer is complete, the DMA controller typically sends an interrupt to the CPU to inform it that the data transfer is done. The CPU can then proceed with processing the data if needed.
Types of transfers that a DMA may control are :
1. Memory to memory transfers (internal to external).
2. Transfers from I/O devices to memory.
3. Transfers from memory to I/O devices.
4. Transfers from/to communications ports and memory.
5. Transfers from/to serial ports and memory.
Some advantages of Direct Memory Access (DMA) :
1. Speed: The data transfers are faster than the CPU-managed data transfers because it doesn’t require CPU involvement in each byte.
2. Efficiency: Its reduces the CPU overhead, by allowing it to focus on other tasks.
3. Parallelism: Multiple DMA channels works simultaneously which improves the system performance in terms of throughput.
4. Minimal delay: System can become more responsive by DMA transfers because it allows CPU to focus on other tasks.
Disadvantages of Direct Memory Access (DMA) :
1. Compatibility issues: DMA configurations may not always be compatible across different hardware systems.
2. Complexity: The complexity increase as we are writing the DMA command block into the memory which contain all the sources and destinations of data transfer that are not contiguous.
3. Limited control: As DMA takes control over the memory bus for data transfers which is not always acceptable because in some situations CPU has to wait for the DMA controller to complete the task.
4. Resource conflicts: In some of DMA capable devices there can be memory conflict when multiple devices attempts to use DMA simultaneously.