


Starvation is a problem where a process runs out of resources in the OS because those resources are being utilized by other processes. That means that a process terminates without completion due lack of resources. Another name for starvation is Lived lock.
Starvation can occur where a process is unable to obtain a necessary resource, such as CPU time, memory, or I/O resources, for an extended period. This typically occurs because other processes or threads are monopolizing the resource, preventing fair access for others. Resource allocation mechanisms within an operating system, like scheduling algorithms, are responsible for managing and preventing starvation.
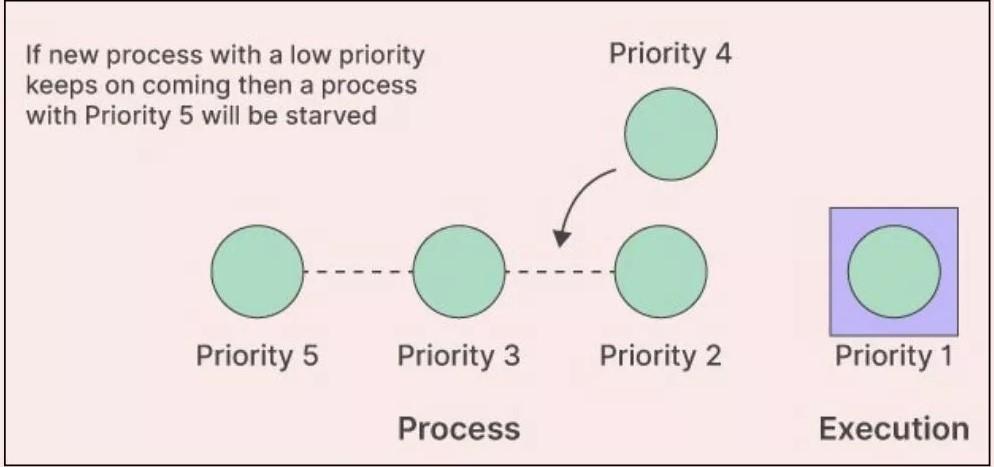
~ One of the main causes of starvation is an unfair scheduling policy. Some scheduling algorithms, such as the Priority Scheduling algorithm, favor high-priority processes over low-priority ones. If the system is busy with high-priority processes, the low-priority processes might be left waiting indefinitely.
~ Another cause could be resource allocation issues. If a certain process holds a resource that another process needs to continue execution, and it doesn't release it, the waiting process can starve
Starvation can be cured using a technique that is regarded as aging. In aging, priority of process increases with time and thus guarantees that poor processes will equally run in the system.
Deadlock is a state where all processes become blocked and the processes are waiting for their resources to be released, whereas in a starvation situation, a process is never given a chance to execute because it is always preempted by a higher-priority process.