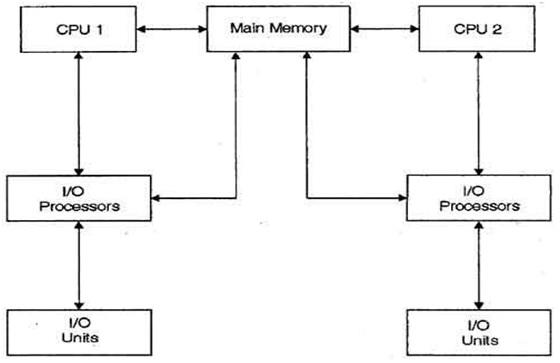
**Multiprocessor Systems and Scheduling**
Multiprocessor Systems**
A **multiprocessor system** consists of two or more processors that share a common physical memory. These processors work simultaneously to execute multiple tasks or processes, improving the system's overall performance. Multiprocessor systems are often classified based on how they handle tasks:
1. **Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP)**:
- All processors share a common memory and operate symmetrically. Each processor has equal access to the operating system and resources.
- Example: Most modern multicore processors in personal computers.
2. **Asymmetric Multiprocessing (AMP)**:
- One processor is the master, and the others are slaves. The master processor controls the entire system and assigns tasks to slave processors.
- Example: Older or specialized systems, such as embedded systems.
3. **Distributed Memory Multiprocessing**:
- Each processor has its own memory. Communication between processors happens through interconnection networks.
- Example: Clustered systems or large-scale distributed computing.
#### **Multiprocessor Scheduling**
Scheduling in multiprocessor systems is more complex than in single-processor systems due to the increased number of processors. The goal is to ensure efficient use of all processors while meeting the required performance and real-time deadlines.
##### **Types of Scheduling in Multiprocessor Systems:**
1. **Process-Level Scheduling**:
- The operating system assigns processes to different processors.
- Challenges: Load balancing, reducing overhead, minimizing processor idle time.
2. **Thread-Level Scheduling**:
- The operating system or an application manages the scheduling of individual threads across processors.
- Challenges: Thread synchronization, sharing data among threads, avoiding contention.
##### **Scheduling Algorithms for Multiprocessor Systems**:
1. **Static Scheduling**:
- Tasks are assigned to processors before execution begins and do not change dynamically.
- Simple and low overhead but inefficient in cases where the workload is unevenly distributed.
2. **Dynamic Scheduling**:
- Tasks are assigned to processors during runtime, allowing for flexibility and better utilization of system resources.
- Examples:
- **Load Balancing**: Ensures that each processor gets an equal amount of work by moving tasks from busy processors to idle ones.
- **Load Sharing**: Each processor takes tasks from a shared queue as they become available.
3. **Partitioned Scheduling**:
- Tasks are divided into groups, and each group is permanently assigned to a particular processor.
- Pros: Reduced overhead.
- Cons: Processors can become underutilized if the workload is not evenly divided.
4. **Global Scheduling**:
- Tasks are placed in a global queue, and any processor can pick tasks from this queue.
- Pros: Ensures better load distribution and utilization.
- Cons: Increased overhead due to task migration and contention for the shared queue.
5. **Real-Time Scheduling**:
- **Hard Real-Time Scheduling**: Ensures that tasks are completed within strict deadlines. Missing a deadline results in failure.
- **Soft Real-Time Scheduling**: Deadlines are important, but the system can tolerate occasional misses.
- Algorithms used:
- **Rate Monotonic Scheduling (RMS)**: Priority-based, where shorter tasks are given higher priority.
- **Earliest Deadline First (EDF)**: The task with the earliest deadline is scheduled first.
6. **Gang Scheduling**:
- A form of scheduling where a set of related processes or threads is scheduled to run simultaneously on multiple processors, ensuring that parallel tasks can be executed without waiting for each other.
7. **Work-Stealing Scheduling**:
- Idle processors steal tasks from busy processors' queues, ensuring dynamic load balancing.
#### **Challenges in Multiprocessor Scheduling**:
- **Load balancing**: Ensuring all processors have roughly equal work.
- **Synchronization overhead**: Ensuring that tasks that depend on each other are properly synchronized.
- **Task migration**: Moving tasks between processors can introduce overhead due to context switching.
- **Cache coherence**: Maintaining data consistency across processors that may have cached copies of shared memory.
Conclusion
Multiprocessor scheduling is key to maximizing the performance of systems with multiple processors. Efficient algorithms and techniques are required to balance workloads and ensure processors do not remain idle while others are overburdened.