


Operation system
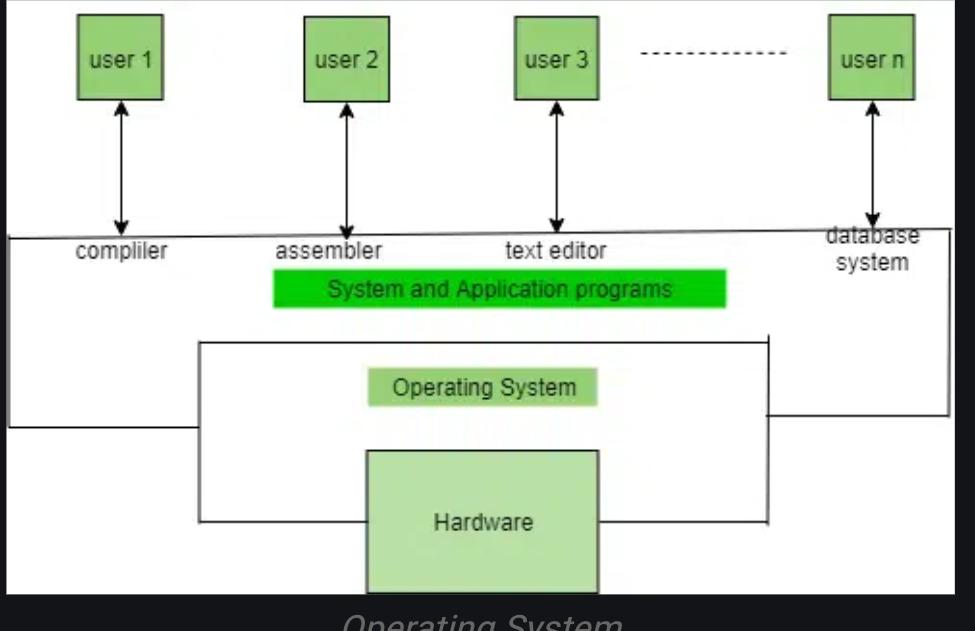
An operating system (OS) is a software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services to computer programs. It acts as an intermediary between computer hardware and user-level applications, controlling the allocation of system resources such as memory, CPU time, and storage.
The primary functions of an operating system are:Process Management: The OS manages the creation, execution, and termination of processes (programs) running on the computer.
Memory Management: The OS manages the allocation and deallocation of memory for running programs.
File System Management: The OS provides a file system, which allows programs to read and write files to storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and flash drives.
Input/Output (I/O) Management: The OS manages input/output operations between devices such as keyboards, mice, printers, and monitors.
Security: The OS provides mechanisms for controlling access to computer resources, such as user authentication, access control, and encryption.
Networking: The OS manages communication between the computer and other devices on a network.
Interrupt Handling: The OS handles interrupts generated by hardware devices, such as keyboard presses or disk completion.
Resource Allocation: The OS manages the allocation and deallocation of system resources such as CPU time, memory, and I/O devices.
Types of Operating Systems:
Single-User, Single-Tasking: Only one user can use the computer at a time, and only one program can run at a time. Examples: MS-DOS, early Mac OS.
Single-User, Multi-Tasking: Only one user can use the computer at a time, but multiple programs can run simultaneously. Examples: Windows 95, Mac OS 8.
Multi-User, Multi-Tasking: Multiple users can use the computer simultaneously, and multiple programs can run simultaneously. Examples: Unix, Linux, Windows NT.
Real-Time: The OS is designed to respond to events in real-time, with predictable and fast response times. Examples: Embedded systems, robotics.
Mobile: The OS is designed for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Examples: Android, iOS.
Examples of Operating Systems:
Windows: Developed by Microsoft, widely used on desktop and laptop computers.
macOS: Developed by Apple, used on Mac computers.
Linux: Open-source, widely used on servers, supercomputers, and embedded devices.
Android: Developed by Google, used on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
iOS: Developed by Apple, used on mobile devices such as iPhones and iPads.
Chrome OS: Developed by Google, used on Chromebooks and other devices.
In summary, an operating system is a crucial software component that enables computers to perform tasks efficiently and securely, while providing a platform for running applications and managing hardware resource.
Hetvi parmar 53003230067