


An Operating System (OS) is the binary of software that manages computer hardware & software resources and it provides common service for programs. Different types of operating systems are designed for different forms and uses.
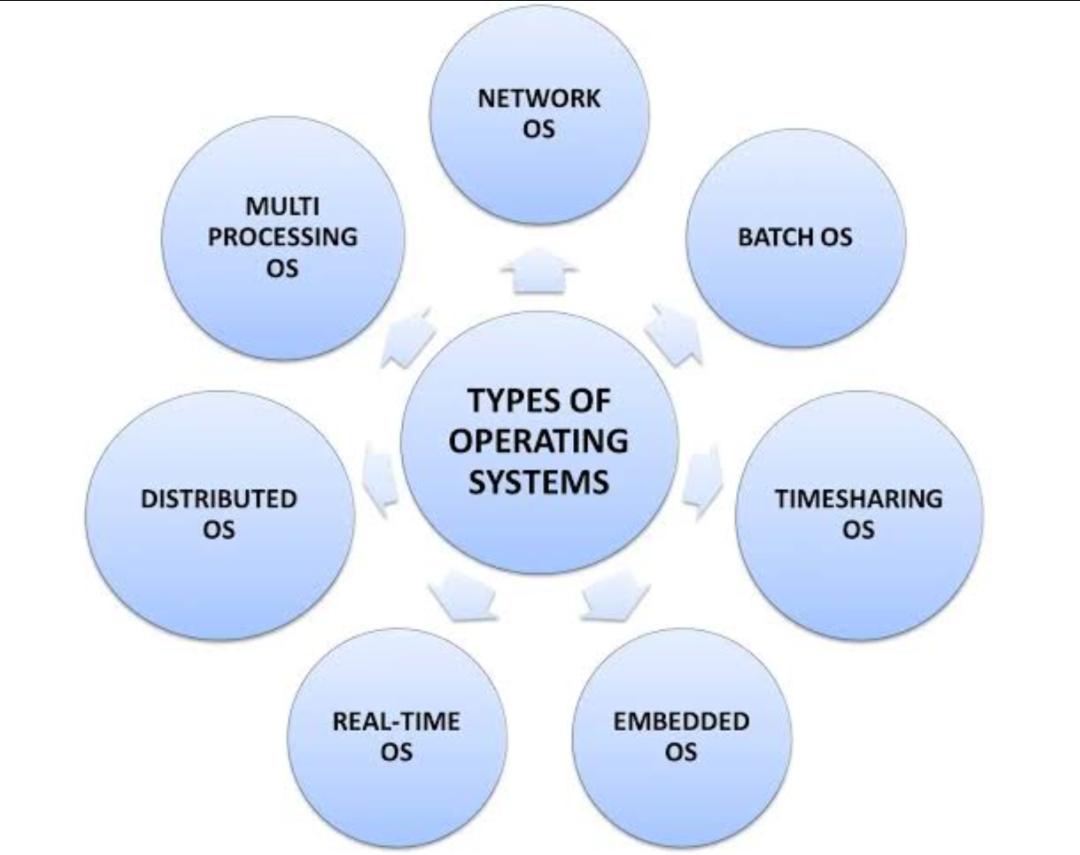
Types of OS are as follows:
Real-time Operating System (RTOS):
RTOS are explicitly tailored to systems that need exact timing and determinism. For example, in real-time environments such as medical equipment or industrial robots or even aerospace applications where response times are crucial. Examples are VxWorks, QNx.
Single-User, Multi-Tasking:
This includes most modern desktop and laptop OSs, such as Microsoft Windows, macOS or various Linux distributions. They enable multiple applications to run concurrently for a single user by utilizing the CPU and memory resources well.
Multi-User:
OS as above are used by large businesses, multiple users to be logged in different times or at the same time with their own login credentials and place. Examples include UNIX ,Linux.
The Distributed Operating Systems:
Distributed OSs -Manage a series of independent computers that seem to the user as one system. This means they make available the sharing of resources, communicating applications and synchronization of processes among networked computers. The examples include Android- Linux OS of Google.
Embedded OS:
Embedded OS are typically designed to run on specific hardware, which is usually low-end in terms of resources (memory and processing power excellent). It is through these sources that energy gets directly delivered to our smartphones, tablets and even the consumer electronic devices of today. Android, iOS and embedded Linux variants stand out.
Mobile Operating Systems:
Developed for smartphones and tablets as well, these OS emphasise touch-screen interfaces along with the power efficiency of mobile devices as well seamless wireless connectivity. Market leader which also includes Android and iOS with app management, security as well a synchronization properties.
Virtualization OS:
A hypervisor is a class of the OS which allows us to create multiple VM on one physical machine and provide control each and every single instance just like we own bare metal servers but actually, these are virtual
machines. VMware is an example of virtual os.
Network Operating Systems (NOS):**
NOS manage and coordinate networked computers and devices, allowing them to share resources like printers, files, and internet connections. They include features for user authentication, file sharing, and network management. Novell NetWare and Windows Server are example of NOS.