


Memory management is the process of controlling and coordinating a computer’s main memory. It ensures that blocks of memory space are properly arranged and allocated so the operating system (OS) , applications and other running processes have the memory they need to carry out their operations.
Types of Memory
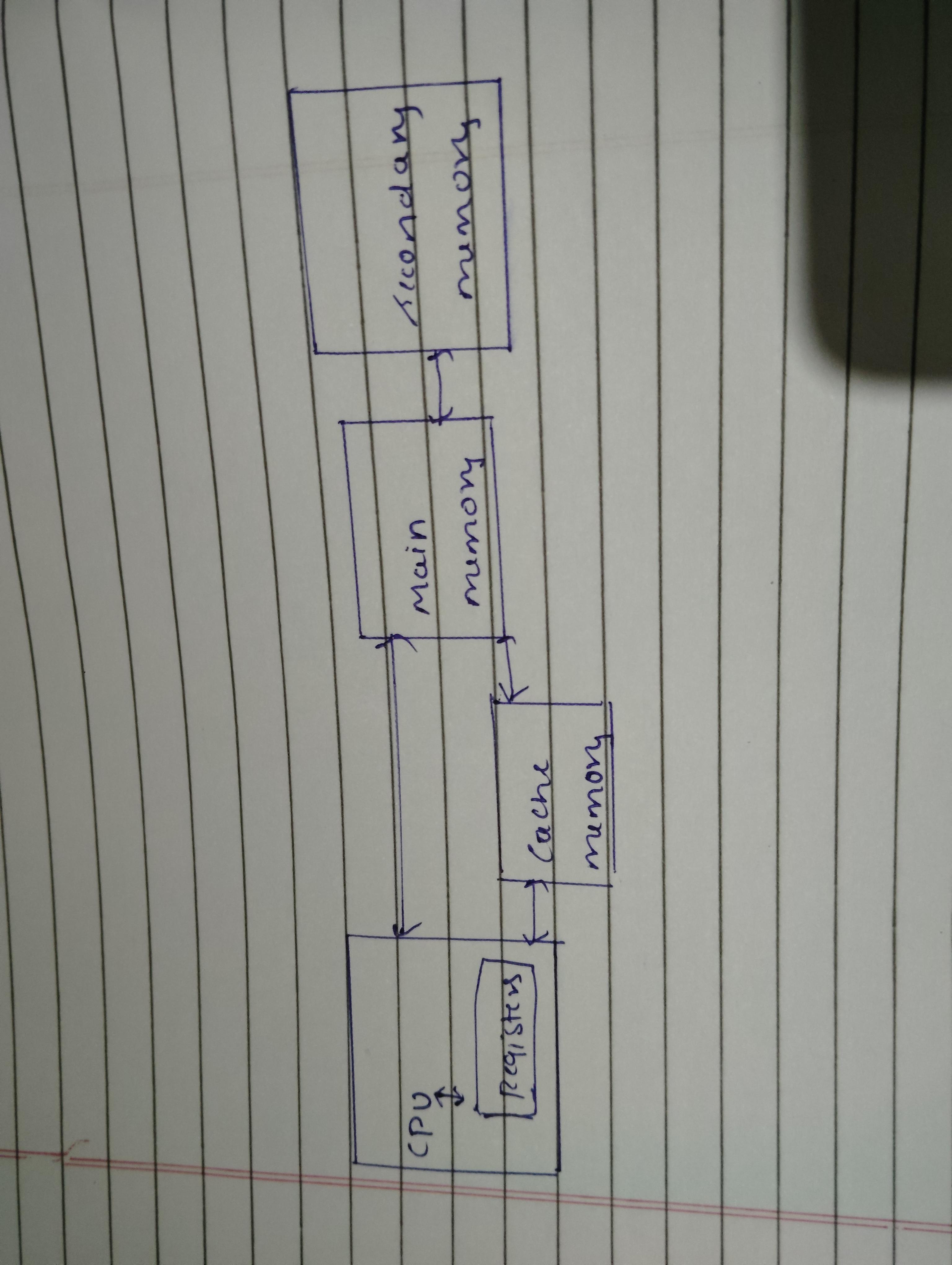
Registers – It is a temporary Storage area built in a CPU access time of register is below 10ns, and registers have lowest capacity that is of few KB of words.
Cache Memory – It is a high speed memory. The purpose of cache memory is to store those program that are repeatedly used or likely to be used in the near future.
Main Memory – It is also known as Primary memory or RAM or Physical memory. The CPU can execute only the data that is present in the Main memory . It is the temporary storage location where data of currently running programs are stored for short period of time.
Secondary Memory – It allows user to store data that can be easily retrieved. This memory cannot be directly used. It can be accessed only by the main memory. For example:- Magnetic tape, magnetic disk, hard disc etc.
Principles for effective memory
Make the common case fast - The principal says that the data which is more frequently used should be kept in faster device. It is based on amdhal's law.
Principle of locality - It is based on locality of references , According to this, the programs tend to reuse data and instruction they have used recently. 90/10 rule comes from empirical Observation:- a program spends 90% of its time in 10% of its code. An Implication of locality is that we can predict with reasonable accuracy what instructions and data a program will use in the near future based on its accesses in the recent past.
Two different types of locality
Temporal locality - States that recently accessed items are likely to be accessed in the near future.
Spatial locality - States that items whose addresses are near one another tend to be referenced closed together in time.