


Deadlock
a deadlock is if 2 processes are waiting for some event to happen and that event never
takes place
eg. if I want to open an account in the bank to receive money but bank requires a minimum
deposit to open an account but I will only deposit the money when I get it from the transfer
that is an example of deadlock
in more technical terms
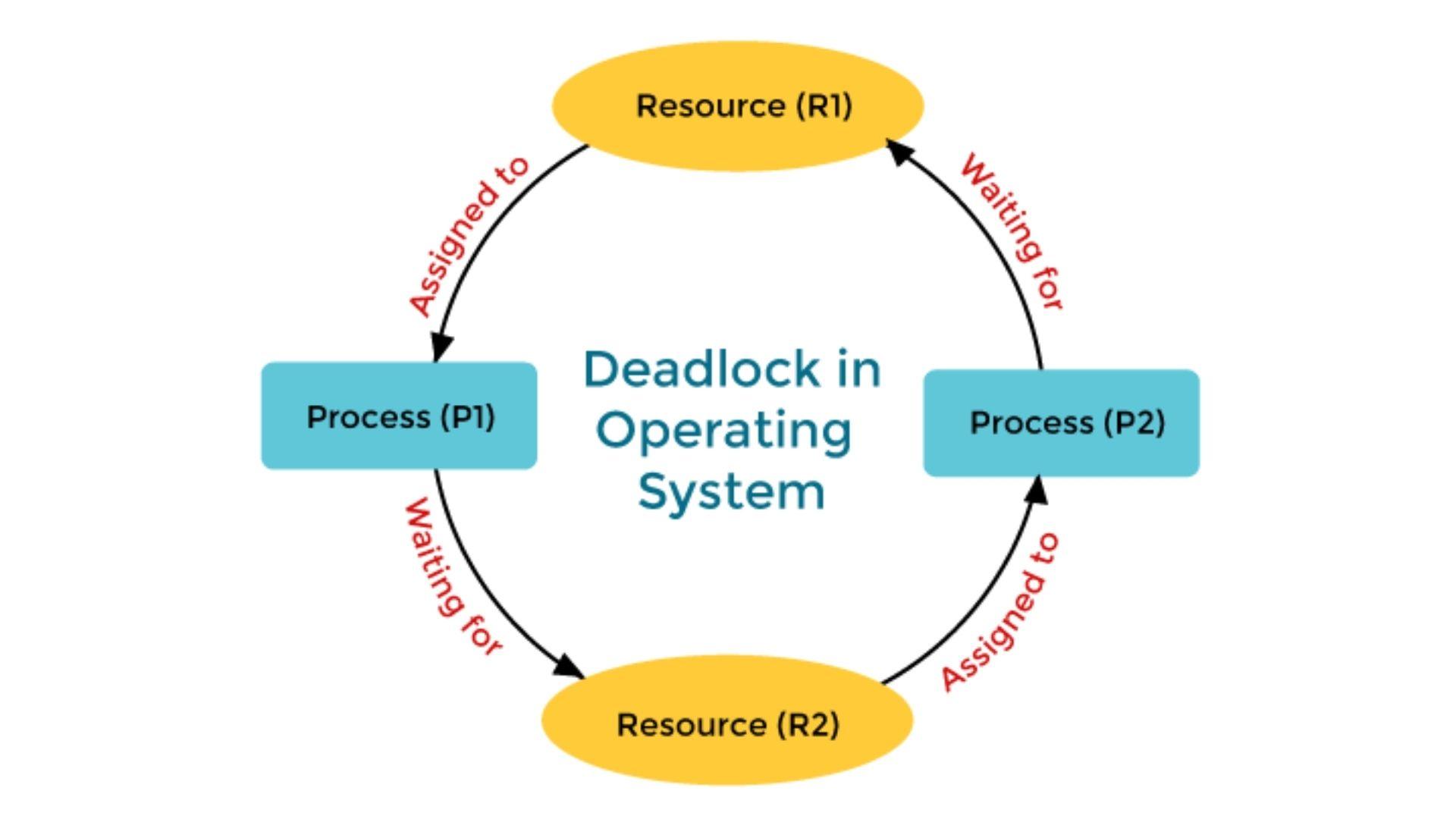
if process 1 locks resource r1 and requires r2 but process2 has locked r2 and requires r1
here atleast one of the processes need to release 1 resource to avoid the deadlock
There are 4 necessary conditions for deadlock: mutual exclusion
no preemption
hold and wait circular wait
1.Mutual exclusion: all the resources must be used by all the processes in a mutually
exclusive manner interleaving is not allowed I.e only one process can hold 1 resource at a
time
2.no preemption: if one process(p1) going on and another process(p2) requires the p1
resource, p1 should not release its resources and hold it because there should not be any
priority system involved and resources should not be switched forcefully only their
respective process can release it
3.Hold and wait: any resources that are currently held by a process should not be released
and that process can require for more resources
4. circular wait: if p1 has r1 and its requesting for r2 and p2 has r2 and its requesting for r1
here both the processes have locked each others resources and therefore its in a circular
manner. Deadlock prevention
1. To avoid mutual exclusion we must use resource in such a way that they can be shared
or the system can handle without exclusive locks
2. To avoid hold and wait the process must require all resources at once if resources are
allocated all must be else none or if additional resource is requested the process must
release all the other resource
3. To avoid preemption the process should release all the resource it currently uses
4. To avoid the circular wait the process must be assigned resources linearly or according
to a hierarchy of priority