


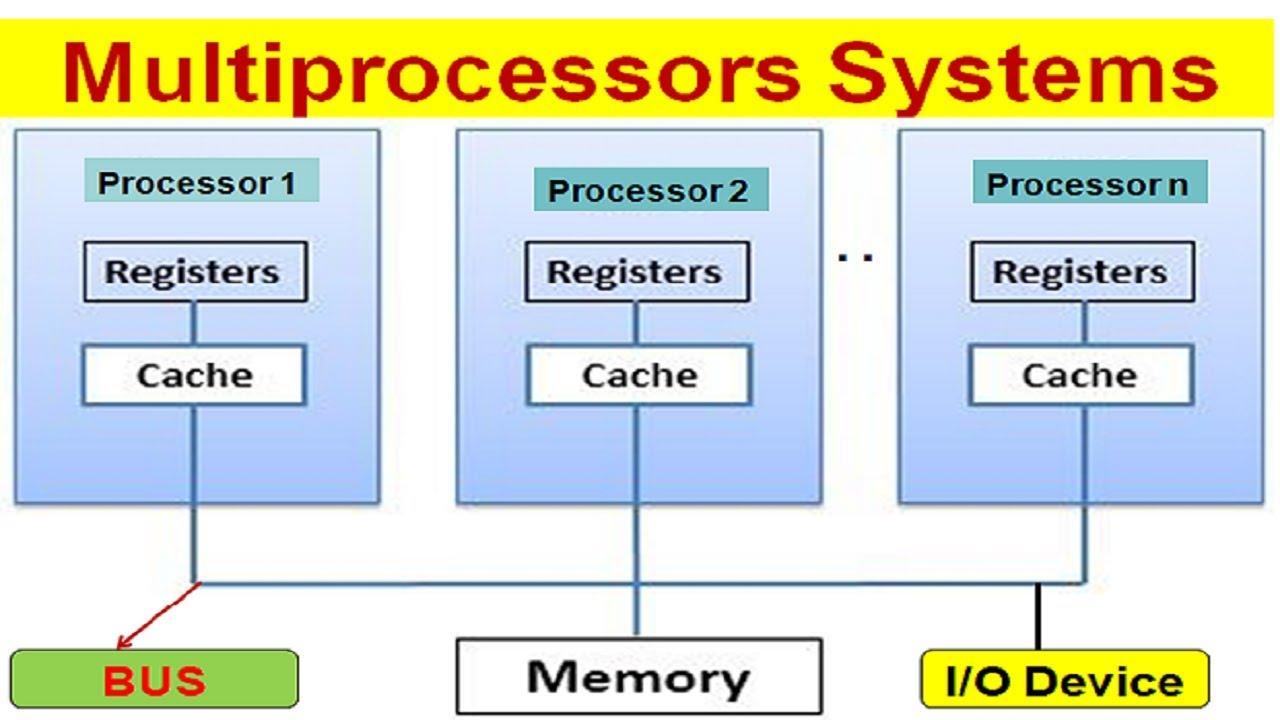
A multiprocessor is a computer system that uses multiple processing units or cores to execute multiple instructions simultaneously, improving overall processing speed and efficiency. In a multiprocessor system, each processing unit or core is a separate processor that can execute its own instructions, and they work together to perform tasks.
Types of Multiprocessors:
Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP): In an SMP system, all processors are identical and share a common memory space. Each processor can execute any task, and the operating system schedules tasks across all processors.
Asymmetric Multiprocessor (ASMP): In an ASMP system, each processor is specialized to perform specific tasks, and the operating system assigns tasks to each processor based on its capabilities.
Massively Parallel Processor (MPP): An MPP system consists of many processing units, often thousands, that work together to perform complex tasks. Each processing unit is connected to a shared memory space.
Characteristics of Multiprocessors:
Parallel Processing: Multiprocessors can execute multiple instructions simultaneously, improving processing speed and efficiency.
Scalability: Multiprocessors can be scaled up or down depending on the processing requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Fault Tolerance: If one processor fails, the system can continue to operate using the remaining processors, ensuring high availability and reliability.
Improved Throughput: Multiprocessors can handle multiple tasks concurrently, increasing overall system throughput.
Advantages of Multiprocessors:
Improved Performance: Multiprocessors can execute tasks faster than a single processor, making them suitable for compute-intensive applications.
Increased Throughput: Multiprocessors can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, increasing overall system throughput.
Better Resource Utilization: Multiprocessors can make efficient use of system resources, such as memory and I/O devices.
Enhanced Reliability: Multiprocessors can provide fault tolerance and high availability, making them suitable for critical applications.
Applications of Multiprocessors:
Scientific Simulations: Multiprocessors are used in scientific simulations, such as weather forecasting, fluid dynamics, and molecular dynamics.
Data Analytics: Multiprocessors are used in data analytics, such as data mining, machine learning, and business intelligence.
Gaming: Multiprocessors are used in gaming consoles and PCs to improve graphics rendering and game performance.
Cloud Computing: Multiprocessors are used in cloud computing to provide scalable and efficient computing resources.
Database Systems: Multiprocessors are used in database systems to improve query performance and transaction processing.
Challenges of Multiprocessors:
Synchronization: Coordinating the execution of tasks across multiple processors can be challenging.
Communication: Exchanging data between processors can be time-consuming and may lead to bottlenecks.
Cache Coherence: Maintaining cache consistency across multiple processors can be difficult.
Programming Complexity: Programming multiprocessors can be complex and requires specialized skills.
In summary, multiprocessors are computer systems that use multiple processing units or cores to execute multiple instructions simultaneously, improving overall processing speed and efficiency. They offer several advantages, including improved performance, increased throughput, and enhanced reliability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they also present challenges, such as synchronization, communication, cache cohere
nce, and programming complexity.