



 AUTHOR : Rushabh Modi
Aim- The focus of the paper is to highlight different methodology by which we can securely and efficiently communicate with the cloud servers.
Abstract- The trend using cloud computing is growing rapidly these days as it provides many luxuries like low cost , ease of accessibility of resource , high performance due to which it becomes forthcoming revolution among Organization[1] . Organization are still not comfortable in using cloud computing as storing private data in cloud can be a major security issue. This paper highlights the importance of cryptographic techniques that can be used to protect the data stored in cloud servers.
INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is in its golden days as it provides variety of services on demand on the basis of pay per use concept .There are various definition of cloud computing given by Organization in their own manner . National institute for Standard and Technology (NIST)[2] defines cloud computing as a model which can enable conveniently, network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) on demand that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Berkeley [3] defines cloud computing as “ to include application software delivered as services over the internet, systems software and the hardware in the data centers that facilitate these services”. There are various type of issues in cloud computing environment which needs to be addressed . According to International Data Corporation (IDC) the most critical issue in cloud environment is security issue . The data travelling in the network must be protected in order to maintain the integrity of the data . This can be done with the help of encryption techniques . Encryption is used to protect the data from the eavesdroppers who can capture the personal data of the organization . One party encrypts the message and the receiving party decrypts the message to obtain the plain text . In addition cipher text should not reveal any information about the original data . There are various encryption schemes available to encrypt and decrypt the data. Authentication of the user is also crucial in order to protect the data and services from unauthorized user. Elliptical curve cryptography technique is used to instantiate the public key protocol , for example implementing digital signatures and key agreements. [4].
Data is outsourced in cloud for the processing purpose so there is need of a system that work on the cipher text So, to overcome this Craig Gentry researcher at IBM proposed the homomorphic encryption on June 25, 2009.Homomorphic encryption scheme allows computation to be performed on cipher text which in turn produces an encrypted result which will be same as computation to be performed on plain text on decryption. In homomorphic encryption data will be encrypted before sending it to the cloud and subsequently, cloud performs computation on this encrypted data so that privacy can be ensured for data on cloud to a certain extent. [5].
AUTHOR : Rushabh Modi
Aim- The focus of the paper is to highlight different methodology by which we can securely and efficiently communicate with the cloud servers.
Abstract- The trend using cloud computing is growing rapidly these days as it provides many luxuries like low cost , ease of accessibility of resource , high performance due to which it becomes forthcoming revolution among Organization[1] . Organization are still not comfortable in using cloud computing as storing private data in cloud can be a major security issue. This paper highlights the importance of cryptographic techniques that can be used to protect the data stored in cloud servers.
INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is in its golden days as it provides variety of services on demand on the basis of pay per use concept .There are various definition of cloud computing given by Organization in their own manner . National institute for Standard and Technology (NIST)[2] defines cloud computing as a model which can enable conveniently, network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services) on demand that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Berkeley [3] defines cloud computing as “ to include application software delivered as services over the internet, systems software and the hardware in the data centers that facilitate these services”. There are various type of issues in cloud computing environment which needs to be addressed . According to International Data Corporation (IDC) the most critical issue in cloud environment is security issue . The data travelling in the network must be protected in order to maintain the integrity of the data . This can be done with the help of encryption techniques . Encryption is used to protect the data from the eavesdroppers who can capture the personal data of the organization . One party encrypts the message and the receiving party decrypts the message to obtain the plain text . In addition cipher text should not reveal any information about the original data . There are various encryption schemes available to encrypt and decrypt the data. Authentication of the user is also crucial in order to protect the data and services from unauthorized user. Elliptical curve cryptography technique is used to instantiate the public key protocol , for example implementing digital signatures and key agreements. [4].
Data is outsourced in cloud for the processing purpose so there is need of a system that work on the cipher text So, to overcome this Craig Gentry researcher at IBM proposed the homomorphic encryption on June 25, 2009.Homomorphic encryption scheme allows computation to be performed on cipher text which in turn produces an encrypted result which will be same as computation to be performed on plain text on decryption. In homomorphic encryption data will be encrypted before sending it to the cloud and subsequently, cloud performs computation on this encrypted data so that privacy can be ensured for data on cloud to a certain extent. [5].
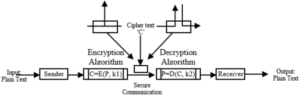
fig 1. The encryption model that shows the flow of data
II.STUDY
Fig 2. Security problems in cloud computing environment
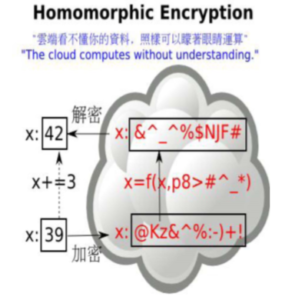
Fig 3. Homomorphic encryption
RSA which is a public key encryption scheme and homomorphic with respect to multiplication and not homomorphic with respect to addition was developed by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman in 1978. In the first round , Bob chooses two large prime numbers p and q and computes n = p*q. Next, bob has to compute Euler’s totient function ij(n), which counts the number of positive integers less than n that are comparatively prime to n. For instance, if n = 6, the integers found by ij(6) are {1, 5}. If n is prime, ij(n) = n í 1. In addition, if n is composed of relatively prime factors, as in our case, ij(n) = ij(p) ·ij(q) = (p í1) ·(q í1). To select his public and private key, Bob chooses two integers a and b such that b = aí1 mod ij(n). (The fact that xij(n) Ł 1 mod n will come in handy for decryption.) The smaller of these two becomes the public key kpub = a, and the other becomes the private key kpr = b. He publishes n and kpub, but keeps p,q, and kpr hidden . Alice can then encrypt a message m by computing c = ma mod n. To decrypt, Bob calculates cb mod n. We can see that decryption works, because cb = (ma) b mod n = ma·a - 1 mod n = m mod n 6 Homomorphism: Furthermore, given two plaintexts m1 and m2 and two corresponding cipher- texts c1 = Encrypt (m1) and c2 = Encrypt (m1) we can compute c1 · c2 = m1 a· m2 a mod n = (m1 · m2) a mod n = Encrypt (m1 · m2) This yields an encryption of the product of our original plaintexts. Thus, the RSA scheme is multiplicatively homomorphic. An ElGamal Algorithm which is also a public key encryption overcomes the difficulty of factoring large integers in security of RSA. This algorithm gives a different cipher text for same plaintext each time it is encrypted which is the main advantage of this algorithm. This algorithm has difficulty of computing discrete logs in a large prime modulus on which its security depends. In ElGamal one of the drawback is that the cipher text is twice as long as the plaintext .Earlier this algorithm was used only for digital signatures, but later it was modified so that it can also be used for encryption and decryption. The strength of this algorithm lies in the difficulty of calculating the discrete logarithm . RSA and ELGamal algorithm exhibits multiplicative homomorphism while Paillier exhibits additive homomorphism by multiplying each component of multiple cipher texts with their corresponding respective components, the decrypted result is equivalent to the addition of the plaintext values . Applications which require computing with encrypted numbers can use this technique i.e. voting schemes and lottery protocols . If a cryptosystem exhibits both additive and multiplicative homomorphism then it is considered as fully homomorphic. Craig Gentry in 2009 first developed a lattice-based fully homomorphic cryptosystem. Fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) enables arbitrary computation on encrypted data. In this cipher texts have some internal noise which grows under homomorphic operations so to overcome this one converts the SHE into an FHE using a refreshing procedure which results in reduction of noise in a given cipher text. This refreshing process is known as bootstrapping because it uses the SHE to homomorphically evaluates its own decryption function .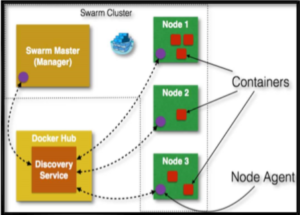
Fig 5. Container clustering
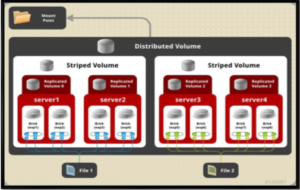 Fig 6. Replication and File Distributed Storage using glusterFs.
In the above figure the file 1 is broken into four chunks and chunk 1 and 3 are stored on brick 1 of server 1 and replicated on brick 2 of same server and chunk 2 and 4 is stored on brick 3 of server 2 and replicated on brick 4 of same server. And accordingly the file is stored on server 3 and 4 as per the above figure.
Relation between cloud computing and containers: Dockers are containers, which ensure the isolation of the working software from the underlying work environment. It packs every dependency, tools and libraries, which are important for the software to run within it. Hence it doesn’t concern whether the system is compatible for the software to run. There are chances that the system might be having some dependency error or missing dependency which is needed for the execution of software. But dockers eliminate this need as they contain each and every dependency within itself. Hence saving the cost and time, which were to be invested for making the working environment able to run the software. Dockers with PaaS: Most of the platform as a service provider like AWS elastic beanstack, openshift or dokku use dockers as a fundamental unit. As we know that PAAS is a layer of automation the coding environment which should be flexible and available on demand with zero downtime or waiting time. Across many IaaS layers, the most important of all (compute) has mostly been shifted from virtual machines to docker containers. Dockers with IaaS: Along with being used in PaaS module of cloud computing, these also relates closely with the IaaS module as well. This is because of the fact that along with providing the coding environment in PaaS, they also provide a computing platform or virtual server completely isolated from its host. One can easily setup a docker cluster which can have webserver installed and can get a fleet of light-weighted webservers on demand which would consume exponentially less resources then a classic virtual server would do. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section II, we have summarized all the research works from which we have got ideas and motivation for this research. In Section III, we have explained this model. In Section IV, we have analyzed the expected outcome of this model followed by Section V concluding remarks of the whole paper and future work.
III.ANALYSIS
Cloud computing can be very reliable and secure if the proper security mechanisms are applied in the crucial areas. According to the study there are three areas into which some sort of cryptographic functionality must be implemented .
First task is of secure authentication , so that no other outside or unauthorized entity is able to access the crucial data. For secure authentication purpose Elliptical curve cryptography can be used in order to efficiently authenticate the user. Elliptical curve cryptography is more efficient then RSA it gives same security with just 163 bit key as 1024 bit RSA key.
Second is in transfer and processing the data . Data can be manipulated or theft while travelling to the server , so good data encryption technique must be implemented to avoid such disaster.
In this case homomorphic encryption can be used to securely transfer the encrypted data to cloud and the processing of the data also carried out in encrypted form . The decryption is only carried out one the users end .
Third place where encryption is needed is while storing the data on the servers. Data from multiple organizations is stored in the same cloud server so there is a chance where one organization can have access to the data from other organization. To overcome this problem we can use docking container that encrypts the data very efficiently and stores it into the glusterFS.
With the use of proper encryption techniques secure cloud computing can be obtained.
METHODOLOGY
Fig 6. Replication and File Distributed Storage using glusterFs.
In the above figure the file 1 is broken into four chunks and chunk 1 and 3 are stored on brick 1 of server 1 and replicated on brick 2 of same server and chunk 2 and 4 is stored on brick 3 of server 2 and replicated on brick 4 of same server. And accordingly the file is stored on server 3 and 4 as per the above figure.
Relation between cloud computing and containers: Dockers are containers, which ensure the isolation of the working software from the underlying work environment. It packs every dependency, tools and libraries, which are important for the software to run within it. Hence it doesn’t concern whether the system is compatible for the software to run. There are chances that the system might be having some dependency error or missing dependency which is needed for the execution of software. But dockers eliminate this need as they contain each and every dependency within itself. Hence saving the cost and time, which were to be invested for making the working environment able to run the software. Dockers with PaaS: Most of the platform as a service provider like AWS elastic beanstack, openshift or dokku use dockers as a fundamental unit. As we know that PAAS is a layer of automation the coding environment which should be flexible and available on demand with zero downtime or waiting time. Across many IaaS layers, the most important of all (compute) has mostly been shifted from virtual machines to docker containers. Dockers with IaaS: Along with being used in PaaS module of cloud computing, these also relates closely with the IaaS module as well. This is because of the fact that along with providing the coding environment in PaaS, they also provide a computing platform or virtual server completely isolated from its host. One can easily setup a docker cluster which can have webserver installed and can get a fleet of light-weighted webservers on demand which would consume exponentially less resources then a classic virtual server would do. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section II, we have summarized all the research works from which we have got ideas and motivation for this research. In Section III, we have explained this model. In Section IV, we have analyzed the expected outcome of this model followed by Section V concluding remarks of the whole paper and future work.
III.ANALYSIS
Cloud computing can be very reliable and secure if the proper security mechanisms are applied in the crucial areas. According to the study there are three areas into which some sort of cryptographic functionality must be implemented .
First task is of secure authentication , so that no other outside or unauthorized entity is able to access the crucial data. For secure authentication purpose Elliptical curve cryptography can be used in order to efficiently authenticate the user. Elliptical curve cryptography is more efficient then RSA it gives same security with just 163 bit key as 1024 bit RSA key.
Second is in transfer and processing the data . Data can be manipulated or theft while travelling to the server , so good data encryption technique must be implemented to avoid such disaster.
In this case homomorphic encryption can be used to securely transfer the encrypted data to cloud and the processing of the data also carried out in encrypted form . The decryption is only carried out one the users end .
Third place where encryption is needed is while storing the data on the servers. Data from multiple organizations is stored in the same cloud server so there is a chance where one organization can have access to the data from other organization. To overcome this problem we can use docking container that encrypts the data very efficiently and stores it into the glusterFS.
With the use of proper encryption techniques secure cloud computing can be obtained.
METHODOLOGY

Fig 7. Combined framework to Ensure Data security.
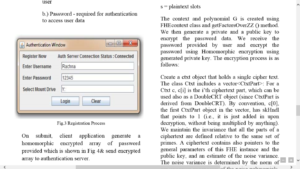
Fig 8. Registration process
On submit, client application generate a homomorphic encrypted array of password provided which is shown in Fig 4& send encrypted array to authentication server.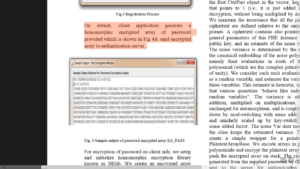
Fig 9. Sample output of password encrypted array EA_PASS
For encryption of password on client side, we setup and initialize homomorphic encryption library known as HElib. We create an encrypted array object ea with a given context and polynomial G. Context is generated with the help of the following parameters: p = Characteristics of plaintext space L = number of levels c = number of columns in key switching matrices k = security parameter d = embedding degree (d ==0 or d==1 => no constraint) s = plaintext slots The context and polynomial G is created using FHEcontext class and getFactorsOverZZ () method. We then generate a private and a public key to encrypt the password data. We receive the password provided by user and encrypt the password using Homomorphic encryption using generated private key. The encryption process is as follows: Create a ctxt object that holds a single cipher text. The class Ctxt includes a vector<CtxtPart>: For a Ctxt c, c[i] is the i’th ciphertext part, which can be used also as a DoubleCRT object (since CtxtPart is derived from DoubleCRT). By convention, c, the first CtxtPart object in the vector, has skHndl that points to 1 (i.e., it is just added in upon decryption, without being multiplied by anything). We maintain the invariance that all the parts of a ciphertext are defined relative to the same set of primes. A ciphertext contains also pointers to the general parameters of this FHE instance and the public key, and an estimate of the noise variance. The noise variance is determined by the norm of the canonical embedding of the noise polynomials, namely their evaluations in roots of the ring polynomial (which are the complex primitive roots of unity). We consider each such evaluation point as a random variable, and estimate the variances of these variables. This estimate is heuristic, assuming that various quantities "behave like independent random variables". The variance is added on addition, multiplied on multiplications, remains unchanged for automorphism, and is roughly scaled down by mod-switching with some added factor, and similarly scaled up by key-switching with some added factor. The noise Var data member of the class keeps the estimated variance. Then we create a simple wrapper for a pointer to a PlaintextArrayBase. We encode arrays in plaintext polynomials and encrypt the plaintext array and we push the encrypted array on stack. The cipher text generated from the supplied password by the user is sent to the server for authentication. Server maintains a copy of ciphertext for equality testing of encrypted password.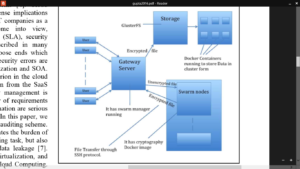
Fig 10. Container based encryption in cloud module
The Above figure is an overall image of how a cryptographic process will carry out using a Docker and Gluster File System. The protocols Docker & GlusterFS are briefed in the coming section but here the main deal is, how a USER sends his or her data to the Gateway server and swarm manager which accepts its data, send it to a random node from its cluster of nodes for the process of encryption, and post encryption in same node, it comes back to the main server again which then is forwarded to the Storage server to replicate and strip it over multiple running Docker containers. Initially, whenever a User sends it data, a Gateway server, which is running a DOCKER SWARM, accepts this unencrypted file from the User. DOCKER SWARM is like a manager of the Docker containers running the Dockers image of encryption and decryption and it is controlled through the Gateway server containing swarm manager. The Next Process is all about encrypting the data. So, the swarm manager sends the unencrypted data from user to the node running Docker cryptography container, which can use AES or RSA or any standard encryption algorithm, encrypts the data and, after encryption, the data is send back to the Gateway server. This incoming and outgoing process or transaction of file is carried out through SSH protocol. Now comes the step where the user data is encrypted but still it needs to be stores such that it is highly available. Now, the encrypted data is sent back at gateway manager which sends the data to another node containing storage manager GlusterFS which is connected to a whole new node containing multiple Docker containers running and the encrypted data will now be distributed and stored on this container cluster using Glusterfs. This way, the file with encrypted data will be stored on multiple docker containers forming a cluster of Storage in order to save data in chunks. Even if the node is compromised, the attacker will not get the data as the containers need to be compromised as well and more over there are number of containers and each container doesn't have the complete data. This Process of encryption and storage of data is extremely resource efficient as Dockers are used to make the whole run in minimal resource. The Docker runs its instance in a single process of the operating system that means the whole encryption process or the storage node runs on a single CPU process, occupying minimal resources. This Process of encryption and storage of data is extremely resource efficient as Dockers are used to make the whole run in minimal resource. The Docker runs its instance in a single process of the operating system that means the whole encryption process or the storage node runs on a single CPU process, occupying minimal resources. Now according to our model, the load on the server for encryption can be properly balanced by increasing the no of nodes of the docker cluster having cryptographic image. And same goes for the storage. Proposed protocol : This protocol compromises of several other protocols. The users interact through the Gateway server through HTTPS protocol to upload their data. The docker container clustering protocol Docker Swarm has its manager setup on this gateway server. So the file uploaded by user is immediately forwarded to a node of the swarm cluster where swarm manager sends a signal to launch a container and the data will be mounted on it and the container will use openssl protocol to encrypt the data via AES, RSA or any other standard encryption algorithm. As soon as the encryption is done, the container terminates and the encrypted data is pulled back to the gateway server and then forwarded to the storage server. The file is transferred from gateway server to other nodes and servers via SSH protocol. The storage server has a cluster of docker nodes running which take disk space from the main system. Glusterfs protocol is used to strip the data into multiple chunks and also replicate it to a backup node if any and store it on the container cluster. In case the user demands to download his data he puts a download request through HTTPS on gateway server and then the gateway server retrieves the file from the storage server and forwards it to its node for decryption, which involves same process as encryption. The decrypted data is pulled back to the gateway server and then available for the user to download. Algorithm 1: Encryption Procedures Procedure: