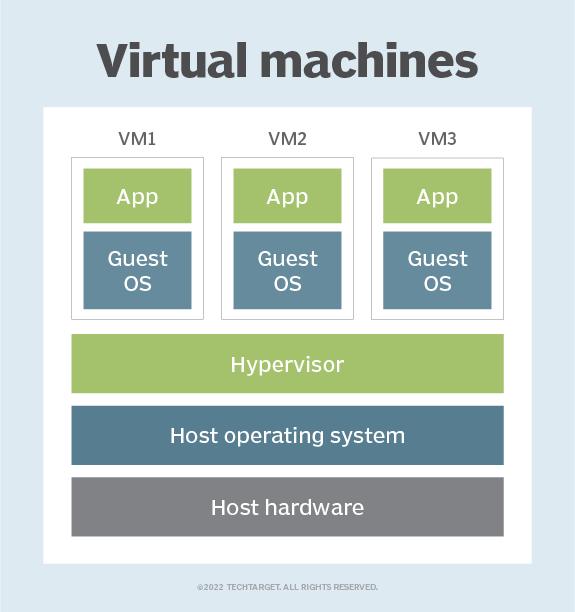
A virtual machine (VM) is a virtual environment which functions as a virtual computer system with its own CPU, memory, network interface, and storage, created on a physical hardware system.
VMs are isolated from the rest of the system, and multiple VMs can exist on a single piece of hardware, like a server. That means, it as a simulated image of application software and operating system which is executed on a host computer or a server.
It has its own operating system and software that will facilitate the resources to virtual computers.
Benefits:
Let us see the major benefits of virtual machines for operating-system users :
• The multiple Operating system environments exist simultaneously on the same machine, which is isolated from each other.
• Virtual machine offers an instruction set architecture which differs from real computer.
• Using virtual machines, there is easy maintenance, application provisioning, availability and convenient recovery.
The role of hypervisors in Virtualization:
Virtualization is the method of creating a software-based, or “virtual” version of a computer with good amounts of CPU, memory, and storage that are “borrowed” from a physical host computer (such as your personal computer) and/or a remote server.
Hosting VMs on a computer requires a specialized type of software called a hypervisor, which manages resources and allocates them to VMs. The hypervisor also schedules and adjusts how resources are distributed based on the configuration of the hypervisor and VMs, including reallocating resources as demands fluctuate.
The hypervisor emulates the computer's CPU, memory, hard disk, network and other hardware resources, creating a pool of resources to allocate to individual VMs according to their specific requirements. The hypervisor can support multiple virtual hardware platforms that are isolated from each other, enabling VMs to run Linux and Windows Server OSes on the same physical host.