


What is Cache Memory?
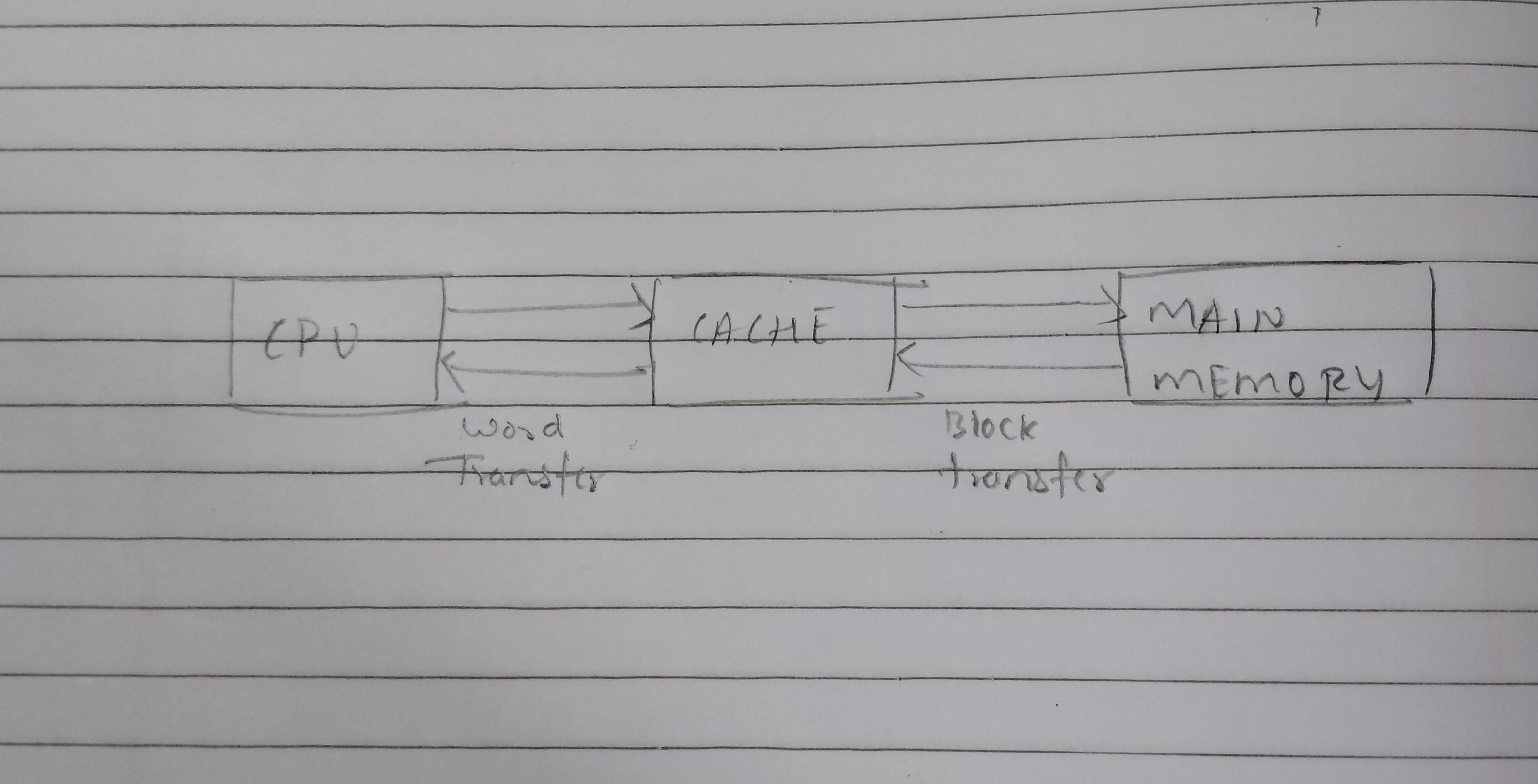
Cache memory is associated with the term high-speed memory. It is comparatively much smaller RAM could work at a much speed than RAM that is the main memory. The cache is accessible to the CPU comparatively faster than the primarily memory the CPU. Therefore, it is employed to run in parallel with a fast processor and at the same time enhance its efficiency.
For example: If there’s a need of money we always check our purse first and if we need more we open our cupboard, even if that much money is not enough then we go to our respective banks. So lets consider bank is a hard disk, cupboard is a RAM and purse as a cache memory, which means whenever there’s an urgent need of money we open our purse that’s a cache memory. Processor takes 35 nanosecond to read from cache memory and 180 nanosecond to read it from RAM.
There are three types of cache memory
L1 cache:
Proximity: The first level of the cache is closest to the cores because most frequently used instructions are stored there.
Speed: It is the fastest type of cache memory designed to match the speed of the CPU.
Size: It is the smallest in size usually ranging from 16kb to 128 kb per core.
Purpose: Compared to the rest L1 cache is accessed most often as it is faster and closer to the and instructions it contains.
L2 cache:
Proximity: This cache is typically located on the CPU chip but it is further away from the cores than l1 cache .
Speed: L2 cache is slower than L1 cache but faster than L3 cache and main memory.
Size: It is larger than L1 cache with size typically ranging from 256kb to a few mb per core.
Purpose: L2 cache is the second level of cache and stores information and instructions that are not present in L1 but required often by the CPU.
L3 cache:
Proximity: L3 cache is usually located on CPU chip but is shared among all the cores in a multi core purpose .
Speed: It is slower than both L1 and L2 but it is still faster than main memory.
Size: L3 is the largest of the three, with size typically ranging from a few mb to tens of mb.
Purpose: It is the final cache before core logic has to go to main memory to fetch the required data It helps to further reduce the latency and improve the efficiency of memory access, particularly in multi-core processors where it can help coordinate and share data among cores.