


Deadlock and Starvation
Introduction:
Deadlock and starvation are the situations where processes are unable to proceed, but they occur in different condition. Deadlock and Starvation are the critical issues related to the process of synchronization in the operating system. Let’s study more about Deadlock and Starvation.
Deadlock:-
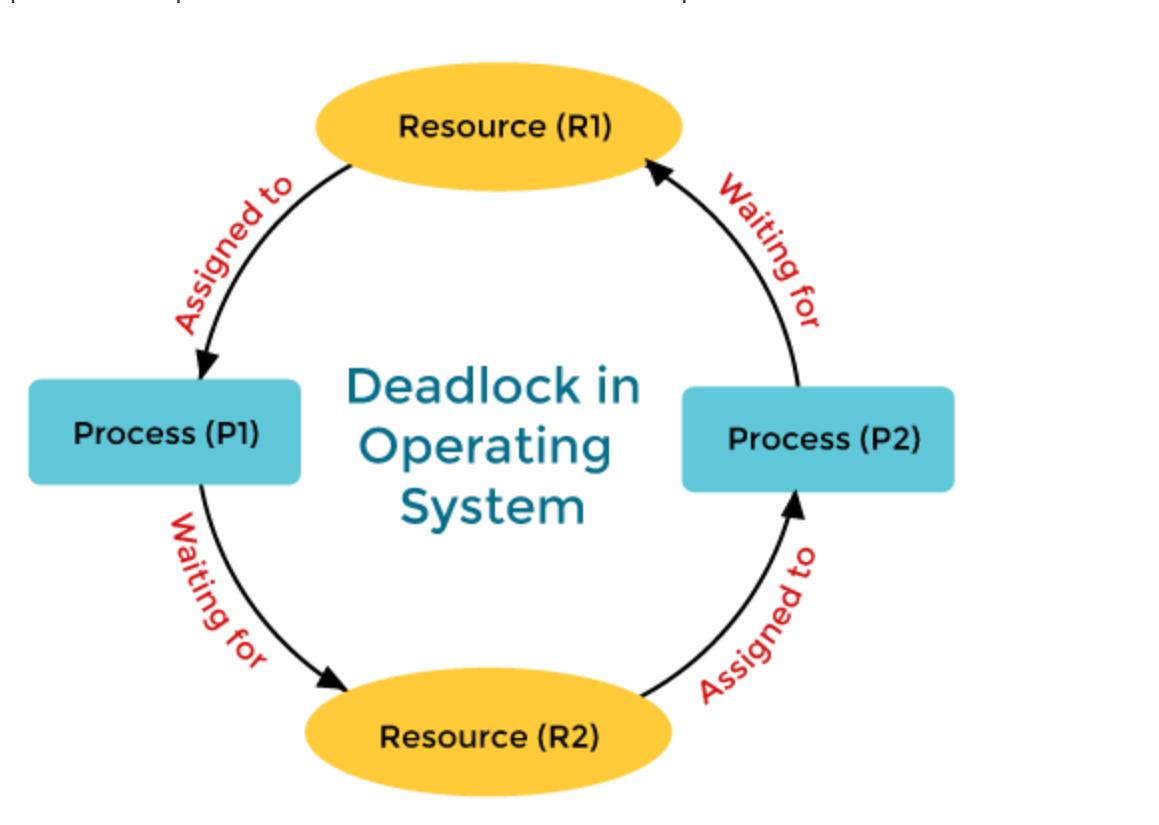
A deadlock is the situation in the operating system where the processes become stuck because each process is waiting for resources held by the other process in the same set, which leads to none of the processes can proceed, and they are indefinitely blocked. Deadlock only happens when 4 conditions which are known as coffman’s conditions, are met simultaneously.
1.Mutual Exclusion: Resources cannot be shared by the processes. Only one process can use the resource at the time.
2.Hold and wait : Processes that are already holding resource can request additional resources that are held by other processes.
3. No premmption : Resources cannot be forcefully take away from the process. Resources must be released voluntarily by the process holding them.
4. Circular wait : There is circular chain of the processes where each process is waiting for a resource held by the next process in the chain.
Example: consider there are two processes, p1 and p2 and two resources, r1 and r2 . If p1 holds r1 and p2 requests r2 while p2 holds r2 and requests r1, neither process can proceed, leading to circular chain and deadlock.
Deadlock Handling:
1. Prevention: By altering the system's resource allocation policy to ensure that at least one of Coffman’s conditions cannot hold.
2. Avoidance: One can use algorithms like Banker’s algorithm to dynamically examine the allocation of resources to ensure that a deadlock state will not occur.
3. Detection and Recovery: By allowing the system to enter a deadlock state and then detecting and recovering from it, often by terminating one or more processes or forcibly taking resources from a process.
4. Ignoring: Often Referred as the "ostrich algorithm," where the system assumes that deadlock will not occur or occur rarely, and no action is taken.
Starvation :
Starvation is also known as indefinite blocking that occurs when a process is perpetually denied access to the resources it needs to process. Unlike the deadlock, where processes are completely stuck , starvation occurs when a process continuously waits while other processes re repeatedly given preference.
Example: In a system where a high-priority process continuously pre-empts resources, lower-priority might never get resources that they need leading to starvation.
Starvation handling:
1. Priority Inheritance : By temporarily raising the priority of the process holding the resources needed by a higer-priority process.
2. Aging: Gradually increasing the priority of waiting process to ensure they eventually acquire the necessary resources.
3. Fair scheduling: by ensuring all the processes get the chance to execute by using algorithms like round-robin scheduling.