Memory management : in an operating system (OS) refers to the process of handling computer memory, including RAM and cache, to optimize system performance and resource utilization. It involves tracking every byte in a computer's memory, whether it is in use or free, and managing the allocation and deallocation of memory blocks to processes and applications. Memory management ensures that each process has enough memory to execute while also ensuring that the system doesn’t run out of memory, which can lead to crashes or performance issues. Key techniques include paging, segmentation, and virtual memory, which allow the system to simulate more memory than is physically available by using disk space. Efficient memory management is crucial for the smooth operation of a multitasking environment, as it ensures that all running processes have the necessary resources without interfering with each other.
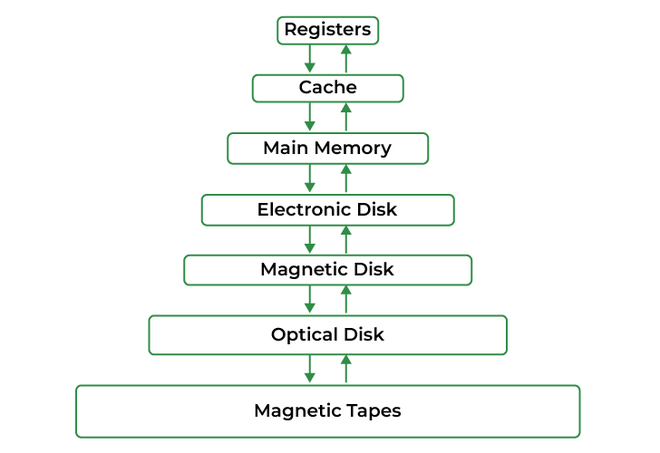
The term memory can be defined as a collection of data in a specific format. It is used to store instructions and process data. The memory comprises a large array or group of words or bytes, each with its own location. The primary purpose of a computer system is to execute programs. These programs, along with the information they access, should be in the main memory during execution. The CPU fetches instructions from memory according to the value of the program counter.