


Definition
Within a process, a thread is a single sequence stream. Because threads have certain characteristics of processes, they are frequently referred to as lightweight processes. Every thread is associated with a single process. A process may have several threads if the operating system allows multithreading. However, threads are only useful if there are several CPUs; otherwise, two threads must context switch for each CPU.
Need for Threads
-Threads run in parallel improving the application performance. Each such thread has its own CPU state and stack, but they share the address space of the process and the environment.
-Threads can share common data so they do not need to use inter-process communication. Like the processes, threads also have states like ready, executing, blocked, etc.
- Similar to a process, a thread can be given priority, with the highest priority thread being scheduled first.
- A Thread Control Block (TCB) is unique to each thread. Similar to the process, the thread experiences a context transition, and the contents of its register are saved in (TCB). Since threads share resources and address space, synchronization is also necessary for the thread's multiple actions.
Components of Threads
Types of Threads
User Level Thread:
It is a type of thread that is not created using system calls. The kernel has no work in the management of user-level threads. User-level threads can be easily implemented by the user. In case when user-level threads are single-handed processes, kernel-level thread manages them. Let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of User-Level Thread.
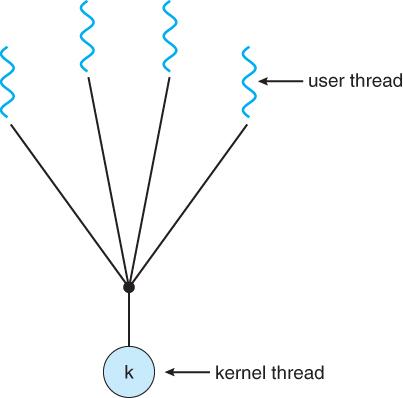
Kernel Level Thread:
It is a type of thread that can recognize the Operating system easily. Kernel Level Threads has its own thread table where it keeps track of the system. The operating System Kernel helps in managing threads. Kernel Threads have somehow longer context switching time. Kernel helps in the management of threads.
Multithreading
A thread is also known as a lightweight process. The idea is to achieve parallelism by dividing a process into multiple threads. For example, in a browser , multiple tabs can be different threads. MS Word uses multiple threads: one thread to format the text, another thread to process inputs, etc. More advantages of multithreading are discussed below.
Multithreading is a technique used in operating systems to improve the performance and responsiveness of computer systems. Multithreading allows multiple threads (i.e., lightweight processes) to share the same resources of a single process, such as the CPU, memory, and i/o devices.