


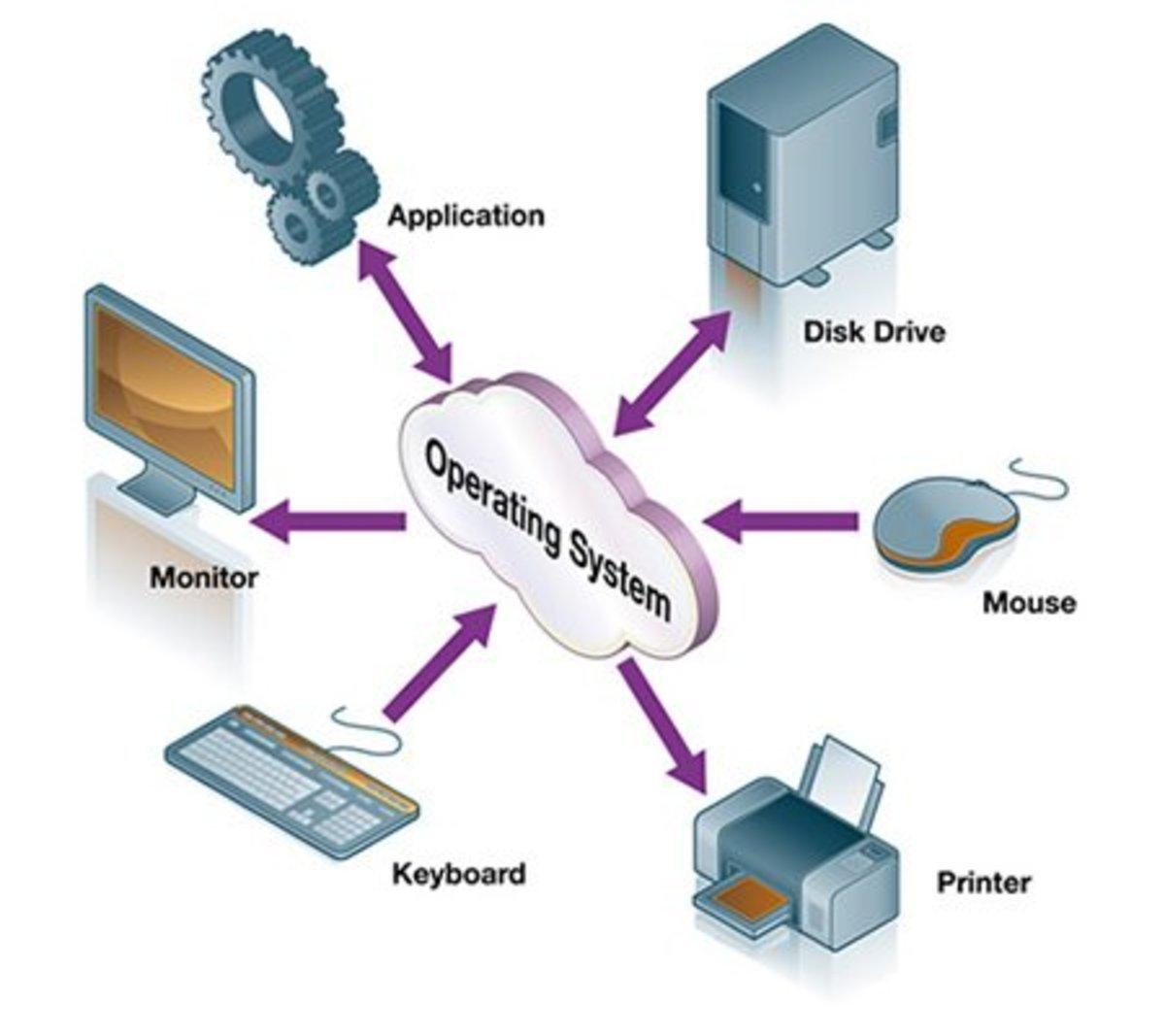
An operating system is a software program that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. It is essential for the functioning of any computer system, from personal computers and smartphones to servers and mainframes.
Process Management: The OS manages processes in a multitasking environment, ensuring that each application gets adequate time and resources to function correctly. This includes process scheduling, creation, and termination.
Memory Management: Efficient memory management is crucial for optimal system performance. The OS allocates memory to various applications and processes, ensuring that each has enough memory to operate while optimizing the overall system memory.
File System Management: The OS manages files on the storage devices, organizing, storing, retrieving, and manipulating files. It also handles file permissions and access rights.
Device Management: The OS manages device communication via their respective drivers. This includes managing input/output devices like keyboards, mice, printers, and storage devices.
Security and Access Control: The OS ensures the security of data and resources by implementing various security measures such as user authentication, access controls, and encryption.
User Interface: The OS provides a user interface, which can be command-line-based (CLI) or graphical (GUI), allowing users to interact with the system easily.
Batch Operating Systems: These systems process batches of jobs without user interaction. Jobs are collected, and similar jobs are batched together to optimize processing time.
Time-Sharing Operating Systems: These systems allow multiple users to share system resources simultaneously. Each user gets a time slice, ensuring efficient utilization of the system.
Distributed Operating Systems: These systems manage a group of distinct computers and make them appear to be a single computer. They are used in distributed computing environments to enhance resource sharing and reliability.
Network Operating Systems: These systems provide services to computers connected to a network, managing network resources, file sharing, and printer access.
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS): These systems are used in environments where time constraints are critical, such as embedded systems, medical devices, and industrial control systems. They guarantee a certain capability within a specified time constraint.
Windows: Developed by Microsoft, Windows is one of the most popular operating systems for personal computers and servers. It is known for its user-friendly interface and extensive software support.
macOS: Developed by Apple, macOS is the operating system for Mac computers. It is known for its sleek design, stability, and seamless integration with other Apple products.
Linux: An open-source operating system, Linux is widely used in servers, supercomputers, and embedded systems. It is known for its robustness, security, and flexibility.
Android: Developed by Google, Android is the most widely used operating system for mobile devices. It is based on the Linux kernel and is known for its extensive app ecosystem.
iOS: Developed by Apple, iOS is the operating system for iPhones and iPads. It is known for its security, smooth performance, and tight integration with the Apple ecosystem.
Operating systems are crucial for the effective functioning of computing devices. They provide a stable environment for applications to run, manage hardware resources efficiently, ensure security and data protection, and offer a user-friendly interface for users to interact with the system. As technology advances, the role of operating systems continues to evolve, adapting to new hardware, software, and user requirements.
Understanding operating systems is fundamental for anyone interested in computing and technology. They are the unsung heroes that ensure our devices run smoothly and efficiently, providing the foundation for modern computing. Whether you are a casual user, a developer, or an IT professional, appreciating the complexities and functionalities of operating systems can enhance your computing experience and open up new possibilities in the ever-evolving tech landscape.