


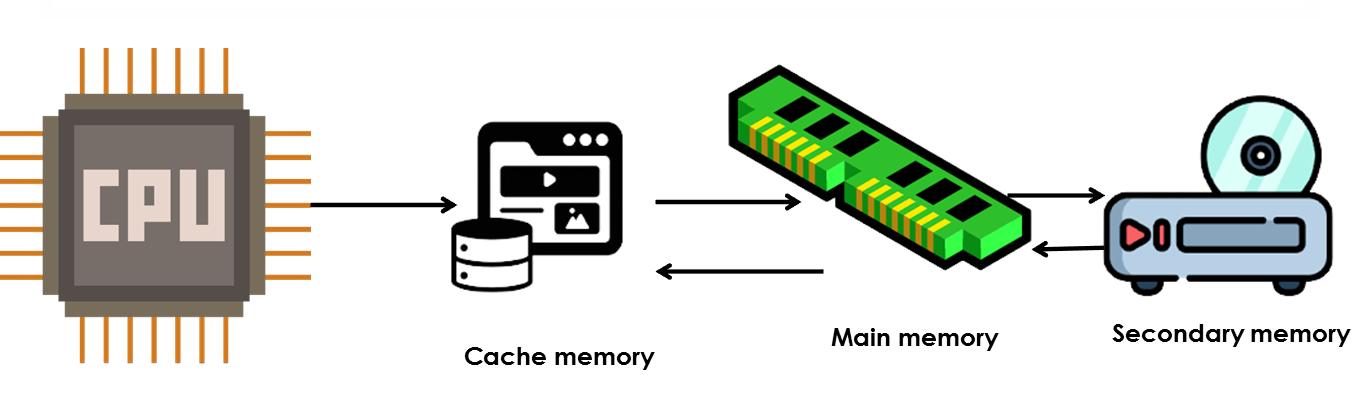
Understanding Cache Memory
Although cache memory is invisible to the OS, it interacts with other memory management hardware.Cache memory is a small-sized type of volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data access to the processor and reduces the average cost (latency) of accessing memory. It operates on the principle of locality of reference, where recently accessed data and instructions are likely to be accessed again in the near future.
Advantages
Cache memory is designed to be much faster than both main memory (RAM) and secondary memory (such as hard drives or SSDs). Here's why:
Proximity to CPU: Cache memory is physically closer to the CPU than main memory or secondary memory. It is typically integrated directly onto the CPU chip or located very close to it on the motherboard. This proximity reduces the time it takes for the CPU to access data and instructions stored in the cache.
Since cache memory has lower access times and is directly accessible by the CPU, programs and instructions stored in cache can be executed more quickly. This is crucial for applications that require rapid data access, such as real-time processing tasks or high-performance computing.
Cache memory offers faster data access times compared to main memory for several reasons:
Cache Hierarchy: Modern computer systems employ a hierarchical cache structure, typically consisting of multiple levels (L1, L2, L3 caches) with varying sizes and speeds. The smallest and fastest cache (L1 cache) is closest to the CPU, providing the lowest access times.
Locality of Reference: Cache memory utilizes the principle of locality of reference, where recently accessed data and instructions are likely to be accessed again in the near future. This reduces the average access time by keeping frequently used data readily available.
Cache memory stores data and instructions that are frequently accessed by the CPU. This strategic storage mechanism enhances CPU performance in several ways:
Reduced Memory Latency: Since cache memory reduces the latency associated with fetching data from main memory or secondary storage, the CPU spends less time waiting for data to be fetched. This allows for smoother and faster execution of programs.
Enhanced Instruction Throughput: By storing frequently used instructions in cache memory, the CPU can execute program instructions in rapid succession. This improves instruction throughput and overall computational efficiency.
Cache Management Strategies
Efficient management of cache memory involves strategies to optimize hit rates (percentage of accesses that result in a cache hit) and minimize miss penalties (time taken to fetch data from slower memory). Key strategies include:
Impact of Cache Memory on System Performance
Cache memory significantly impacts the overall performance of operating systems by: