


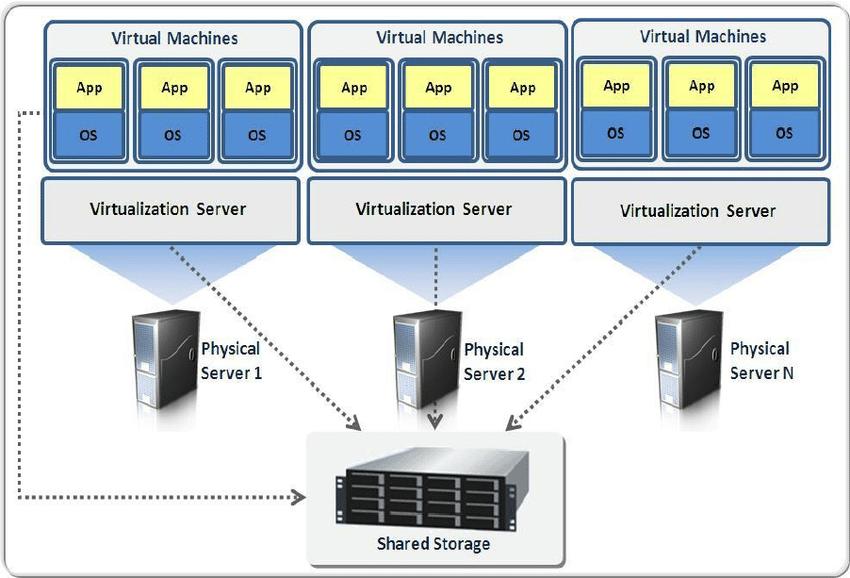
Virtualization is a technology that allows a single computer or server to run multiple operating systems or sessions of a single OS simultaneously. It provides a way to optimize hardware usage and enables businesses and individuals to deal with legacy applications effectively.
In virtualization, a virtual machine monitor (VMM) or hypervisor is used to manage and support virtual machines (VMs). The VMM runs on top of or is incorporated into the host operating system. Each VM emulates hardware devices and can run a separate operating system. The VMM handles the communication between each OS and the underlying hardware, such as the processor, storage medium, and network.
Virtual machines can communicate with each other through virtualized network connections when necessary. This allows different applications running on different operating systems to coexist on a single platform.
There are two main approaches to virtual machine architecture: process virtual machines and system virtual machines.
A variant of system virtual machines is the hosted VM, where the VMM is built on top of an existing host operating system. The hosted VM relies on the host OS for device drivers and lower-level services. An example of a hosted VM is the VMware GSX server.
Virtualization technologies offered by companies like VMware and Microsoft are widely used in server and desktop environments to run multiple operating systems efficiently and maximize hardware utilization.