


File management in an operating system refers to the ways in which the OS handles and organizes files on storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and flash drives. Here are some key aspects of file management:
1. File Systems: A file system is a way of organizing files on a storage device. Common file systems include FAT, NTFS, HFS, and ext4.
2. File Naming: Rules for naming files, such as allowed characters, length limits, and naming conventions.
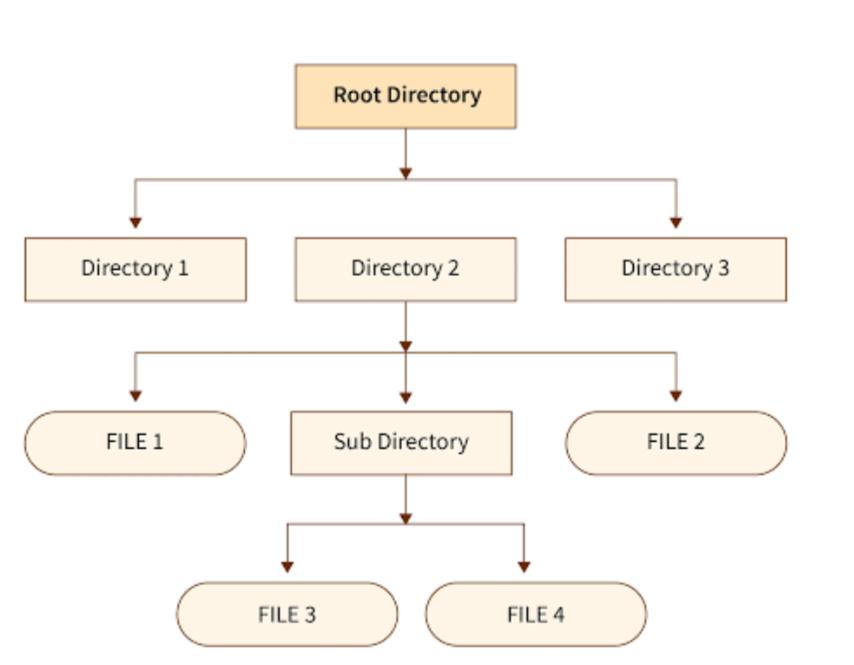
3. File Structure: How files are organized in a hierarchical structure of directories and subdirectories.
4. File Permissions: Control over who can access, modify, or delete files.
5. File Storage: How files are stored on disk, including allocation methods and disk formatting.
6. File Retrieval: How files are retrieved from disk, including file searching and indexing.
7. File Editing: How files are modified, including file locking and version control.
8. File Backup: Creating copies of files to prevent data loss.
9. File Compression: Reducing file size to save storage space.
10. File Encryption: Protecting files from unauthorized access.
File management operations include :
• Create: A new file is defined and positioned within the structure of files.
• Delete: A file is removed from the file structure and destroyed.
• Open: An existing file is declared to be “opened” by a process, allowing the
process to perform functions on the file.
• Close: The file is closed with respect to a process, so that the process no longer
may perform functions on the file, until the process opens the file again.
• Read: A process reads all or a portion of the data in a file.
• Write: A process updates a file, either by adding new data that expands the size of the file or by changing the values of existing data items in the file.