


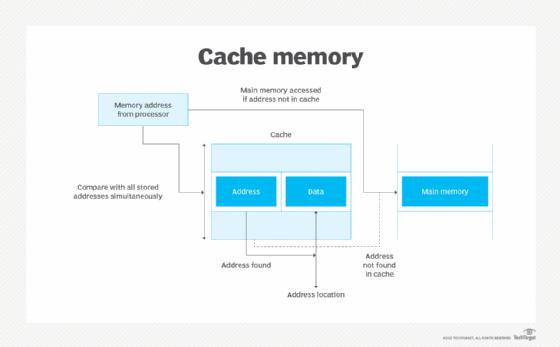
Cache memory is a small, high-speed storage area in a computer. The cache is a smaller and faster memory that stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. There are many different independent caches in a CPU, which store instructions and data. The most important use of cache memory is that it is used to reduce the average time to access data from the main memory.
By storing this information closer to the CPU, cache memory helps to speed up the overall processing time. Cache memory is compartively much faster than the main memory (RAM). When the CPU needs data, it checks the cache first . If the data is there, the CPU can access it quickly. If not, it must fetch the data from the slower main memory.
Cache memory plays a important role in modern computing, acting as a bridge between high-speed CPU registers and slower main memory (RAM). Its purpose is to store frequently accessed data and instructions to accomplish more quickly processing and enhance overall system performance.
Function and Importance
Cache memory operates on the principle of locality, which assumes that programs tend to access the same data or instructions multiple times within a short period. By storing this data closer to the CPU than main memory, cache reduces the time it takes to fetched info, thereby speeding up the processing. This is achieved through faster access times and lower time delay compared to RAM.
Types of Cache
Modern computers feature several levels of cache:
L1 Cache: Located closest to the CPU cores, L1 cache is small but extremely fast, providing rapid access to frequently used data and instructions.
L2 Cache: located between L1 cache and RAM, L2 cache is larger but slightly slower compare to L1. It serves as a secondary buffer to accommodate additional data and instructions.
L3 Cache: Some systems include a third level of cache (L3), which is larger and slower than L2 but still faster than main memory. L3 cache is often shared among CPU cores.