


Operating Systems Segmentation in operating system is a memory management technique where main memory is divided into different size segments and there are no restrictions on the ways to divide the program. The actual code or data in a module can be part of one segment -that is, the segments represent logical (rather than physical) units(score.hs).
The main purpose of segmentation is to improve management and utilization of memory by allowing programs including data structures that have logical part in different sizes contiguously load into physically non-contiguous pockets. This can be especially helpful in cases like large programs that do not fit entirely as one continuous block of memory.
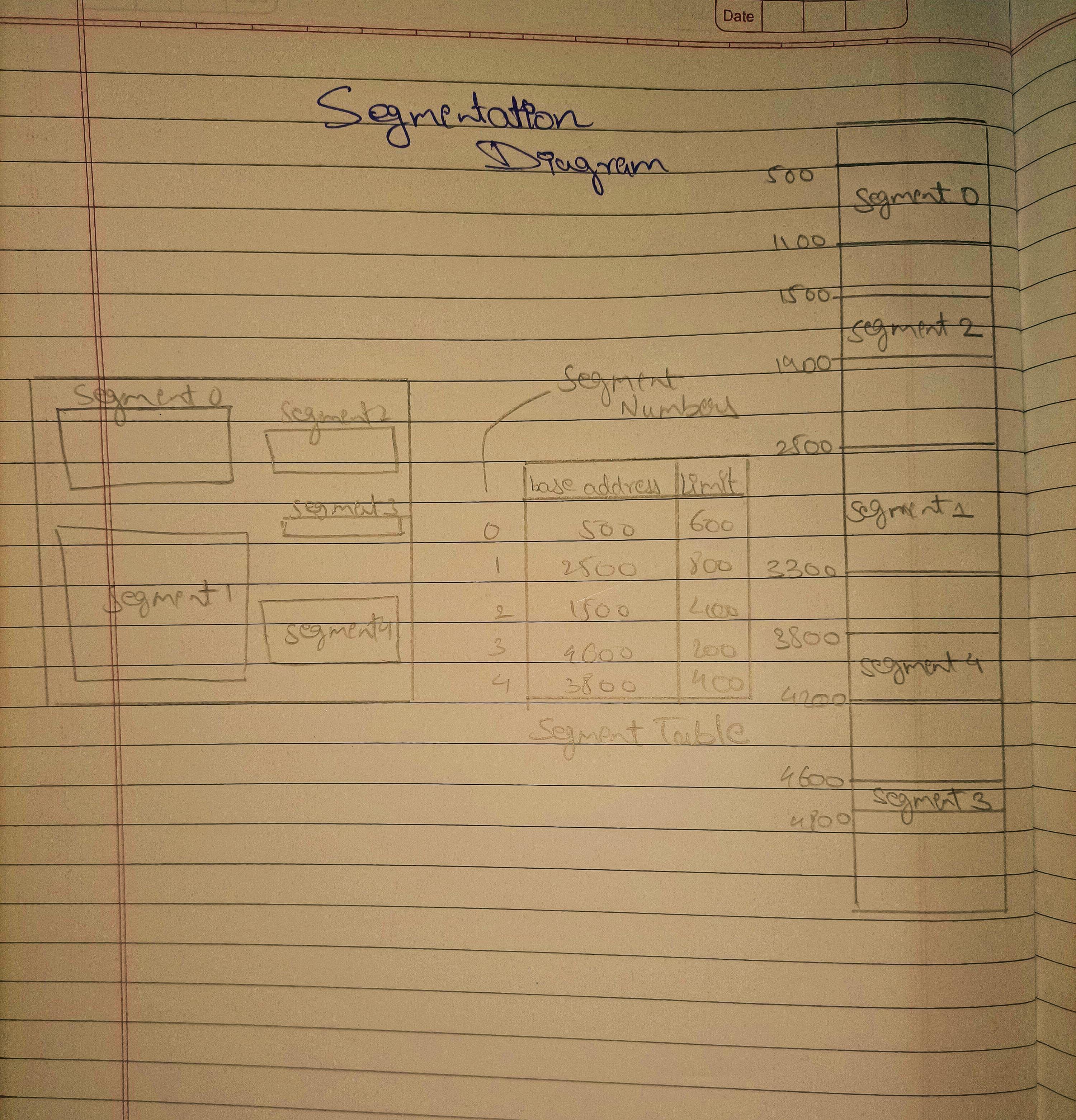
Segments are generally created using data organization, such as segmented by the size or type of the information stored. Each segment is also given an unique number called the Segment Number or base address of its lexical object in memory.
Programs will ask access to the segments, specifying which segment number they want together with an offset value that is a where in that segment. The operating system converts this logical address to a physical address by adding the base-address of that segment.
1.Flexible Segmentation: It offers dynamic allocation and deallocation of segments which helps in better utilization of memory available.
2.Sharing: Common segments can be shared by many processes, which decreases the total memory needed. It provides access control, to protect segments from unauthorized access by using appropriate hardware and software level of mechanisms.
3.Simple extension: The fact that new sections can be effectively added means programs easier to expand without them having to reload into ongoing squares
1.External Fragmentation: The free spaces left between allocated segments goes on reducing with time, and as a result there occurs scattering of some part-sized places over main memory.
2.Fragmented Allocation: Each allocation of memory, even de-allocation or reallocation involves bookkeeping about various details (size and the segment allocated) which makes managing system resources complex to ensure each resource is reused efficiently.
3.Complex Address Translation: The translation of logical addresses to physical addresses is more complicated relative to the same function in other techniques such as paging.
4.Segmentation is extensively used in combination with another popular method of memory management called Paging (segment and Page) for better efficiency given their capabilities on different demands, especially seen both together because Operating System nowadays are modern one i.e. like Windows or Linux.