


1. Deadlock
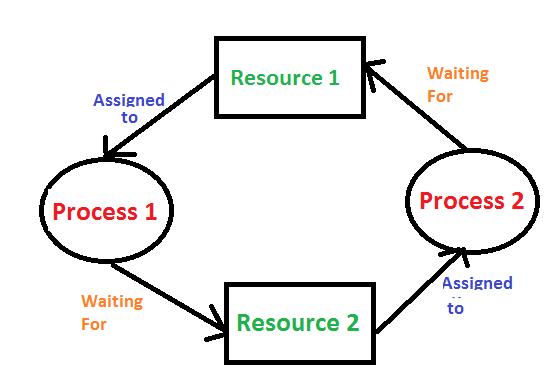
Deadlock in an operating system occurs when a set of processes become stuck because each process is waiting for a resource that another process holds, and none of the processes can proceed. This situation usually arises in multi-process systems where processes share resources such as files, memory, or devices. The four necessary conditions for deadlock, often referred to as Coffman’s conditions, are mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. If all these conditions hold simultaneously, the system can enter a deadlock state. Deadlocks can be addressed through prevention, avoidance, or detection and recovery methods. Prevention involves designing the system to negate one or more of the Coffman conditions, while avoidance uses algorithms like Banker’s Algorithm to ensure the system never enters an unsafe state. Detection and recovery involve allowing the deadlock to occur but having mechanisms to identify and resolve it by terminating processes or rolling them back.
2.Starvation
Starvation occurs in an operating system when a process waits indefinitely to gain access to a resource it needs, even though the resource is available at times. This typically happens in scheduling algorithms that favor certain processes over others, like when a low-priority process is continually preempted by higher-priority processes. Starvation is a significant problem because it can lead to reduced system performance and inefficiency. Solutions to starvation include using aging, a technique where the priority of a waiting process is gradually increased, ensuring that every process eventually gets a chance to execute. By incorporating aging into scheduling algorithms, the operating system can prevent starvation by ensuring that processes waiting for resources for a long time are eventually given access, thus maintaining system fairness.