


■ CRISP-DM Methodology: A Complete Guide to Data
Mining Success
Introduction
In today’s digital era, data is considered the new oil. Every industry, from banking and healthcare to
retail and government, relies on data-driven decision-making to stay competitive. However, raw
data alone does not create value—it must be systematically processed, analyzed, and transformed
into actionable insights. This is where the CRISP-DM methodology comes into play. CRISP-DM
(Cross-Industry Standard Process for Data Mining) is the world’s most widely adopted framework
for data mining and data science projects. It provides a structured and repeatable process that
ensures data initiatives are aligned with business goals, technically sound, and ultimately beneficial
for decision-making.
History of CRISP-DM
The CRISP-DM model was developed in 1996 as part of a European Union-funded project. The
initiative was led by SPSS (now IBM), NCR Systems Engineering, and Daimler-Benz, along with
several other partners. At the time, data mining was emerging as a powerful tool, but many
organizations lacked a standardized approach. CRISP-DM was introduced to fill this gap by
providing a cross-industry, vendor-neutral, and flexible framework. In 2000, the first official version
of CRISP-DM was published and quickly gained worldwide adoption. Even after two decades,
CRISP-DM remains the de facto standard in data mining and data science projects.
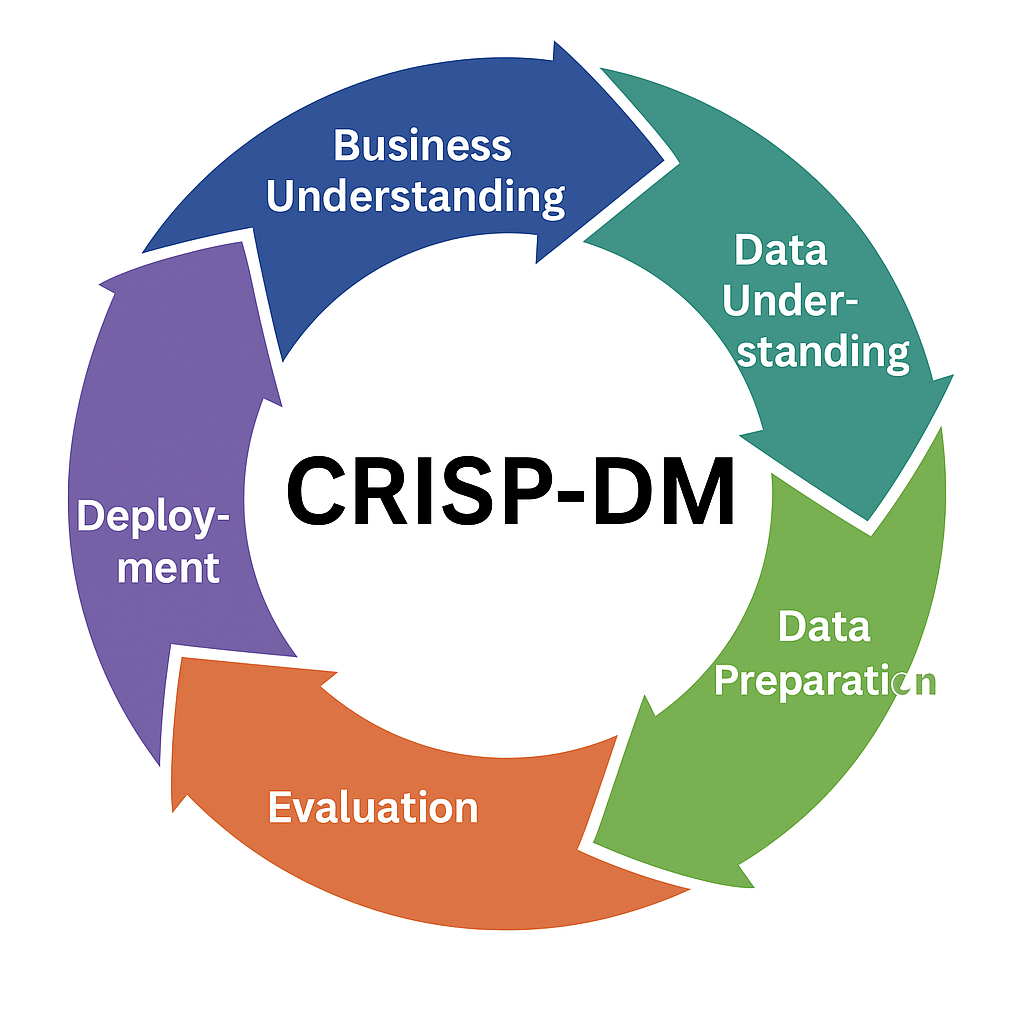
The Six Phases of CRISP-DM
The CRISP-DM methodology is divided into six interrelated phases. Unlike a linear process,
CRISP-DM is iterative, meaning teams can move back and forth between phases as needed. 1.
Business Understanding – Define goals and objectives. 2. Data Understanding – Collect and
explore data. 3. Data Preparation – Clean and structure data. 4. Modeling – Apply algorithms and
build models. 5. Evaluation – Check performance and ensure objectives are met. 6. Deployment –
Deliver solution for real-world use.
How CRISP-DM Works in Practice
The power of CRISP-DM lies in its flexibility and iterative nature. It starts with business goals,
ensuring that data science is not just a technical exercise but a solution to a real-world problem.
The back-and-forth movement between data understanding, preparation, and modeling allows
continuous improvement. Deployment and monitoring ensure that insights are sustainable and
actionable. In practice, teams often revisit earlier phases when they uncover new patterns or when
business requirements evolve.
Purpose of CRISP-DM
• Provides a roadmap for data mining projects. • Ensures alignment between business and
technical teams. • Minimizes risks by identifying issues early in the process. • Promotes
reproducibility and scalability in data projects.
Benefits of CRISP-DM
1. Industry-Neutral – Works across different domains: healthcare, finance, retail, education, and
government. 2. Structured and Repeatable – Reduces uncertainty by following clear steps. 3.
Flexibility – Iterative process allows adjustments at any stage. 4. Business-Focused – Ensures that
the end solution delivers real business value. 5. Widespread Adoption – Enables better
collaboration and communication among stakeholders.
Real-Life Examples
• Retail: Predicting which products sell most during holiday seasons. • Banking: Detecting
fraudulent transactions in real time. • Healthcare: Predicting patient readmissions based on clinical
data. • Education: Identifying students at risk of failing and providing early interventions.
Conclusion
The CRISP-DM methodology has stood the test of time as the gold standard in data science and
data mining. By providing a structured, iterative, and business-driven process, it helps organizations
turn raw data into meaningful insights that guide better decisions. As data continues to grow in
scale and complexity, CRISP-DM remains relevant because it balances technical rigor with
business needs. For anyone aspiring to build a career in data science or for organizations aiming to
harness the power of data, mastering CRISP-DM is not just useful—it is essential.