Starvation occurs when a process in the OS runs out of resources because other processes are using it. This is a problem with resource management while Operating systems employ aging as a scheduling approach to keep them from starving. It is one of the most common scheduling algorithms in batch systems. Each process is assigned a priority. The process with the highest priority is to be executed first and so on. Here we will be discussing a major problem related to priority scheduling and its solution.
What is Starvation?
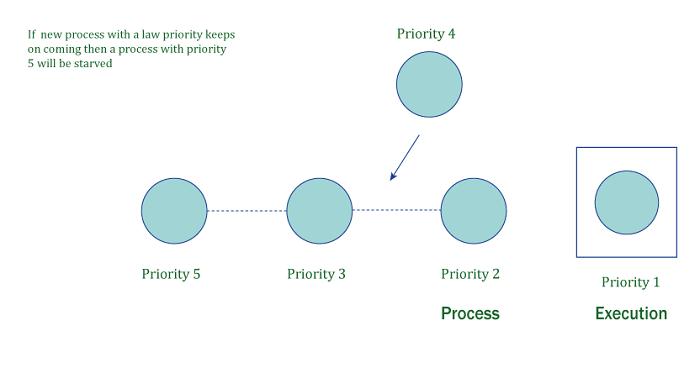
Starvation or indefinite blocking is a phenomenon associated with the Priority scheduling algorithms, in which a process ready for the CPU (resources) can wait to run indefinitely because of low priority. In a heavily loaded computer system, a steady stream of higher-priority processes can prevent a low-priority process from ever getting the CPU. There have been rumors that in 1967 Priority Scheduling was used in IBM 7094 at MIT, and they found a low-priority process that had not been submitted till 1973.
Reasons of Starvation:
- There are not enough resources available to everyone during starvation, and processes begin to lose priority.
- If higher-priority processes continuously monopolize the processor, a lower-priority operation might have to wait indefinitely. As a result of the low-priority programs not communicating with anything, Starvation cannot result in a standstill.
- A process may have to wait a lengthy period if a random selection of processes is employed due to non-selection.
- Since starvation is a failsafe way to break a deadlock, the way it impacts the system as a whole is far more crucial.
- Starvation may result if a process is never given the resources it needs to be executed due to poor resource allocation decisions.
How to Control Starvation?
- Resource distribution can be handled by an impartial manager. In an effort to prevent starvation, this resource manager allocates resources equitably.
- It is best to avoid choosing processes at random when allocating processors or resources because this promotes starvation.
- The principles of Ageing, where a process’s priority increases the longer it waits to prevent starvation, should be included in the resource allocation priority system.