


A thread is the smallest unit of the code execution in a process
A program may have multiple processes and a process may have multiple threads execution processes occur in the cpu. A thread is a basic utilization of cpu
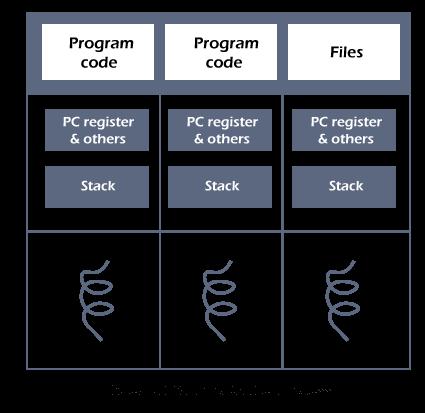
A thread consists of
• Thread id
• A program counter
• Register set
• Stack
It also shares code section, data section and other operating system resource with the same process, a process is heavy weight if it performs a single thread but multiple threads will allow multiple task execution
Benefits of multithreading
• Responsiveness: eg in a Gui one thread handles frontend Ui and another handles backend process
• Improved performance: significant boost in application as multiple threads run parallelly decreasing the time
• Resource sharing: threads of the same process also share code section, data section and other operating system resource with the same process, making the communication between them easy
• Scalability: multithreads handle increasing workloads significantly by dividing tasks among each other
Multi-threading
Types of threads
• User thread: used by developers and are supported above the kernel and managed without kernel support
• Kernel thread: supported and managed directly by operating system
For a system to exits there should be relationship between user and kernel threads
Types of relationships:
1. One to one
2. Many to one
3. Many to many
One to one: 1 user thread maps to 1 kernel thread, provides more concurrency than many to 1 as it allows a new thread to run when a thread makes blocking call, allows multiple threads to run inn parallel on multiprocessors. But creating a user thread forces to create a kernel thread and overhead of creating kernel thread can cause burden in the application
Many to one: many user threads access 1 kernel thread and the thread management is done by thread library in user space and makes it efficient. But if one of the many user threads makes a blocking system call then the kernel thread will be blocked and entire process will be blocked. Because one thread accesses 1 kernel at a time multiple threads don’t run in parallel on multiprocessors because 1 kernel only runs 1 process.
Many to many: Many user threads are mapped to many kernel threads and number of kernel threads may be specific to an application or machine, developers can create multiple user threads and they run in parallel in a multiprocessor and when a user thread asks for a blocking system call the kernel can execute another thread for execution
DONE BY AARON DSOUZA
53003230005