


The DNS is a great technology that allows us to use the internet the way we know currently. It resolves domain names to their IP addresses, and we get our answers almost instantly. But the DNS resolution is a complicated process that could involve many DNS servers placed far away from each other, and it takes time. There is a way to reduce the DNS queries and save time – DNS cache.
The DNS cache (also known as DNS resolver cache) is a temporary DNS storage on a device (your computer, smartphone, server, etc.) that contains DNS records of already visited domain names (A records for IPv4 addresses, AAAA records for IPv6, etc.). It keeps those records, depending on their time-to-live (TTL).
Each time you visit a website, its addresses will be saved inside this temporary database of records to facilitate a later revisit.
Basically, the DNS cache is how your device is trying to save effort and time and skip a long DNS lookup by answering a DNS query with a DNS record that is already inside the temporary DNS cache.
We need DNS cache to get a faster response for DNS query for domain names that we have already visited recently in the past.
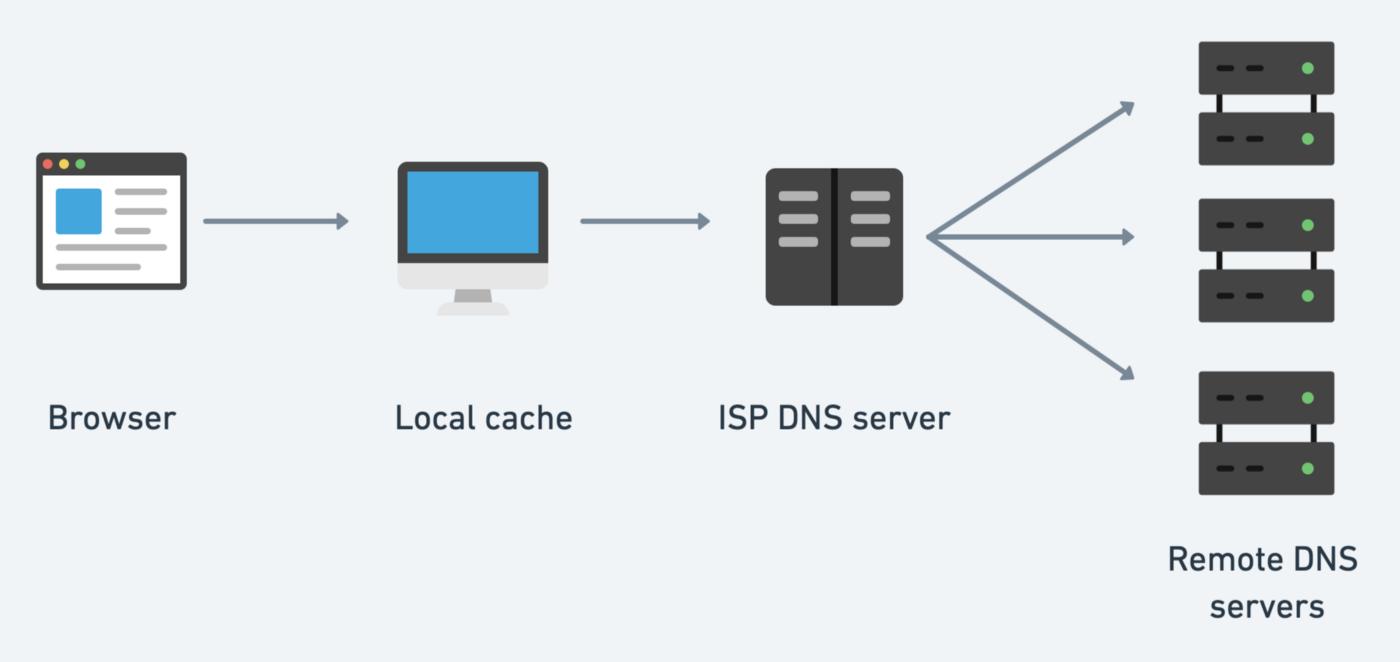
Both the device, that the user is using (his or her computer) and the multiple DNS resolvers, that the request reaches, have DNS cache and they can resolve the domain if it is still in their cache memory. If not, the DNS query will need to follow the long way to the root server who will direct to the TLD servers and then they will direct to the authoritative name server for the domain name to finally get the answer.
Each time a user performs a DNS lookup, its device will first check inside the internal DNS cache that is part of the OS. There is a table of DNS records inside the DNS cache, their values, and the time they could be kept (TTL). The TTL value is set by the DNS administrator of each domain name, and it is the time limit that each DNS record has. After the time runs out, a new query is required.
If the DNS query can be resolved from the DNS cache, the user will get their answer, and they can visit the site they desired.
If no, the query will travel to a recursive DNS server. There are many DNS recursive servers out there. Like for example, there are inside your Internet Service Provider. They also have a cache that works in the same way. If the answer can be found there, the user will get it and resolve the domain.
If no, the query will travel to an authoritative nameserver to get the answer.
When it gets the answer, the DNS record or records will be saved in each of the DNS caches of the recursive DNS servers on the way and inside the user’s device, too, for the period that the TTL value indicates.
Next time a new query starts for the same domain name, your device will repeat the process. If not so much time has passed, there is a high chance that the DNS record your device needs is still inside this temporary memory, and the query gets answered instantly.