


Deadlock
Definition
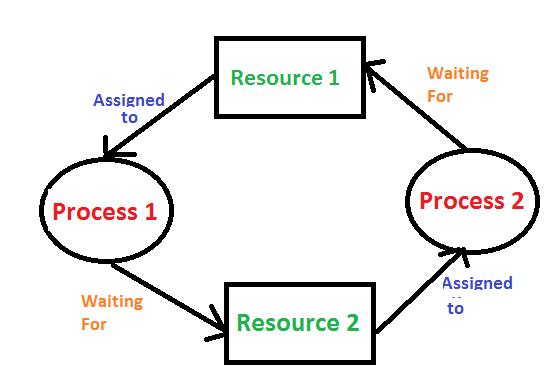
A deadlock is a situation in which the operating system has a set of processes that are permanently blocked. Each process in the set is waiting for a resource that is held by another process in the set. This circular wait completes a cycle, making each process unable to proceed.
Conditions for Deadlock
Deadlock can occur only if all the following four conditions hold simultaneously:
Mutual Exclusion: At least one resource has to be held in a non-shareable mode.
Hold and Wait: There has to be a process holding at least one resource, waiting to get additional resources from other processes.
No Preemption: Resources cannot be taken forcefully from the processes having those resources; these have to be released voluntarily.
Circular wait: That is, a set of processes must exist such that every process is waiting for a resource that the next process in the set possesses. In effect, they are all waiting for each other, forming a circle.
Prevention and Avoidance
Prevention: Design resource allocation policy of the system such that at least one of the above necessary conditions cannot occur. For example, require that all resources a process will need be requested at once.
Avoidance: Run-time resource-allocation state is dynamically analyzed to ensure that a circular wait condition can never occur. Banker algorithm is an example of a dead lock avoidance algorithm.
Starvation
Definition
Starvation, also known as indefinite blocking, is a situation where a process is indefinitely deprived of the resources necessary for its execution to proceed. This usually happens due to improper resource allocation policies.
Causes
Priority Scheduling: In priority scheduling-based systems, the low priority processes starve if high-priority processes are continuously given the system's resource.
Resource Allocation: If the resources are always granted to certain processes, other processes never get the resources they require to execute.
Prevention
Aging: Gradually increase the priority of the waiting process in the queue for the resource. This ensures that even the low priority processes eventually do get the required resources.
Fair Share Scheduling: Resources must be allocated fairly between the processes. It can be implemented using a round-robin scheduling mechanism or other algorithms that ensure that each process gets a fair slice of resource time.
Conclusion
Thus, deadlock and starvation are the two major issues of operating systems that bring inefficiency into them and might eventually lead to the collapse of a system. While it is related in some respect, deadlock implies that execution of the processes has completely come to a halt because of contention for resources; on the other hand, starvation means the processes are indefinitely delayed. Resource management policies and algorithms turn out to be essential in preventing this problem in order to enable the smooth running and efficiency of a system.