


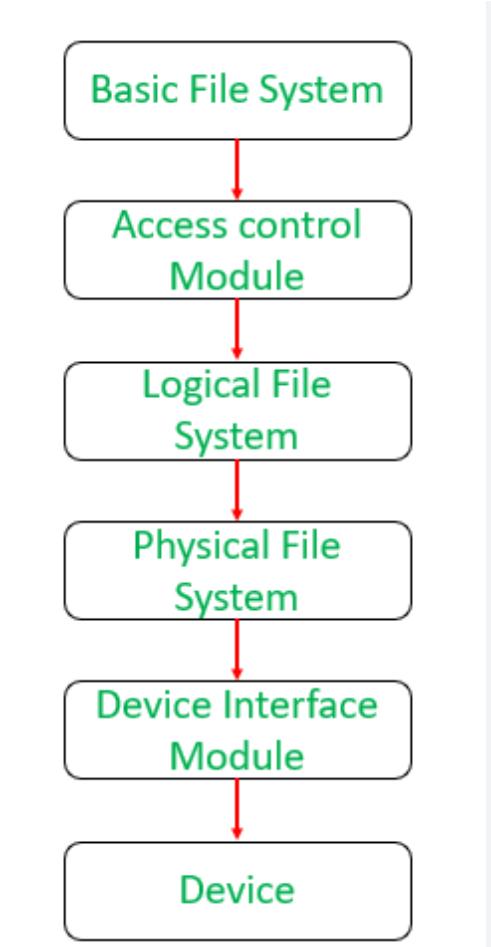
File management is a critical aspect of any operating system (OS), playing a fundamental role in the efficient and organized handling of data. This process involves the creation, manipulation, storage, and retrieval of files within a computer system. Effective file management ensures that data is stored in an organized manner, accessible when needed, and protected from unauthorized access.
At the core of file management is the file system, which dictates how data is stored and retrieved. Common file systems include NTFS, FAT32, and ext4, each with its own structure and features. For instance, NTFS, used in Windows operating systems, supports large file sizes, file permissions, and encryption, while ext4, used in many Linux distributions, offers features like journaling and large volume support.
File management begins with the creation of files and directories. When a file is created, the operating system allocates space on the storage medium and assigns a name and metadata to the file. This metadata includes information such as the file size, creation date, and access permissions. Directories, or folders, are used to organize files into hierarchical structures, allowing users to manage and locate files efficiently.
The manipulation of files includes various operations such as reading, writing, copying, moving, and deleting. File operations are managed through system calls and user interfaces. For example, a user can create a new document using a word processor, which interacts with the OS to allocate space and manage file attributes. Similarly, file copying involves duplicating the file's data and metadata to a new location, while moving a file changes its location without altering its content.
Access control is another crucial aspect of file management. Operating systems implement permission systems to regulate who can access or modify files. Permissions can be set at various levels, including read, write, and execute permissions. In multi-user environments, these permissions help maintain security and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Storage management, which includes the allocation and deallocation of disk space, is vital for efficient file management. The OS uses techniques such as file fragmentation and defragmentation to optimize storage usage. Fragmentation occurs when a file is broken into pieces scattered across the disk, which can slow down access times. Defragmentation reorganizes these pieces to improve performance.