


Memory management in an operating system (OS) is essential for efficiently allocating, managing, and optimizing memory resources. Here are the key points:
1. Memory Hierarchy:
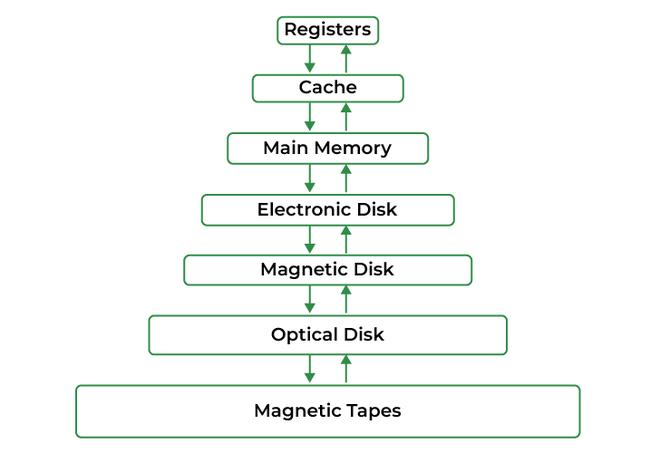
- The memory hierarchy consists of registers, cache, main memory (RAM), and secondary storage. Each level differs in speed, size, and proximity to the CPU.
2. Allocation Strategies:
- Memory allocation can be contiguous, where memory is allocated in a single block, or non-contiguous, where memory is allocated in separate blocks, helping to reduce fragmentation.
3. Paging and Segmentation:
- Paging: Divides memory into fixed-size pages, mapped to physical memory frames, allowing efficient use of memory and supporting virtual memory.
- Segmentation:Divides memory based on logical divisions of a program, offering more flexibility but potentially increasing fragmentation.
4. Virtual Memory:
- Allows the OS to extend physical memory using disk space, enabling larger programs to run on systems with limited RAM. This is managed through paging.
5. Memory Protection:
- Protects the memory space of each process from being accessed by others, ensuring system stability and security.
6. Fragmentation:
- Internal Fragmentation:Wasted space within allocated memory blocks.
- External Fragmentation:Scattered free memory blocks, making it difficult to allocate large contiguous spaces.
7. Swapping:
- Swapping moves processes between main memory and disk to free up RAM, though it's more disruptive and used when memory is insufficient.
8. Garbage Collection:
- An automatic memory management process that frees memory no longer in use by applications, commonly used in languages like Java.
9. Page Replacement Algorithms:
- When physical memory is full, algorithms like FIFO (First-In, First-Out) and LRU (Least Recently Used) determine which page to replace to optimize memory usage.
10. Kernel Memory Management:
- The OS kernel requires dedicated memory management to handle critical system functions while maintaining security and stability.
Effective memory management ensures efficient use of memory, supports multitasking, prevents issues like fragmentation and memory leaks, and contributes to overall system performance and security.